Fig. 2. SAMC is the only mitoSAM carrier and is required for OXPHOS and oxidative tricarboxylic acid (TCA) metabolism.
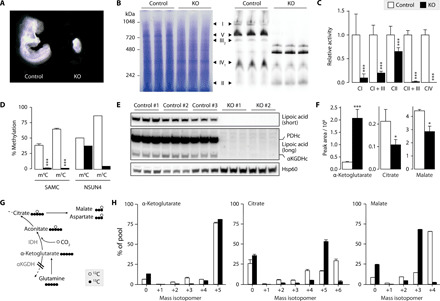
(A) Wild-type (Slc25a26+/+) and Slc25a26 homozygous KO (Slc25A26−/−, KO) embryos at embryonic day 8.5. (B) Blue Native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) immunoblot on MEF mitochondrial extracts with Coomassie staining (left) and an antibody mix against OXPHOS complex subunits (right) (n = 3). (C) Isolated respiratory chain complex activities (n = 3). (D) Bisulfite pyrosequencing on 12S mt-rRNA from MEFs (n = 3), or control (white) and Nsun4 KO (black) hearts (n = 1), targeting 4′-methylcytosine m4C909 (m4C) or 5′-methylcytosine m5C911 (m5C). (E) Western blot analysis on mitochondrial lysates from MEFs, showing lipoylation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase E2 subunits. Hsp60 is the loading control. Short and long exposures are shown (n = 3). (F) Intracellular levels of α-ketoglutarate, citrate, and malate in MEFS cultured in 12C medium (n = 3). (G) Schematic of metabolite labeling obtained during reductive carboxylation of glutamine-glutamate–derived α-ketoglutarate. Circles represent 13C (black) and 12C (white) atoms. IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase. (H) Mass isotopomers of α-ketoglutarate, citrate, and malate in MEFs cultured in 13C medium (n = 3). Bar graphs show means + SD. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 with two-sided Student’s t test of KO (black) against MEF control (white) cells. (C) and (D) show pooled data from three control and two KO MEF cell lines (n = 3).
