FIGURE 1.
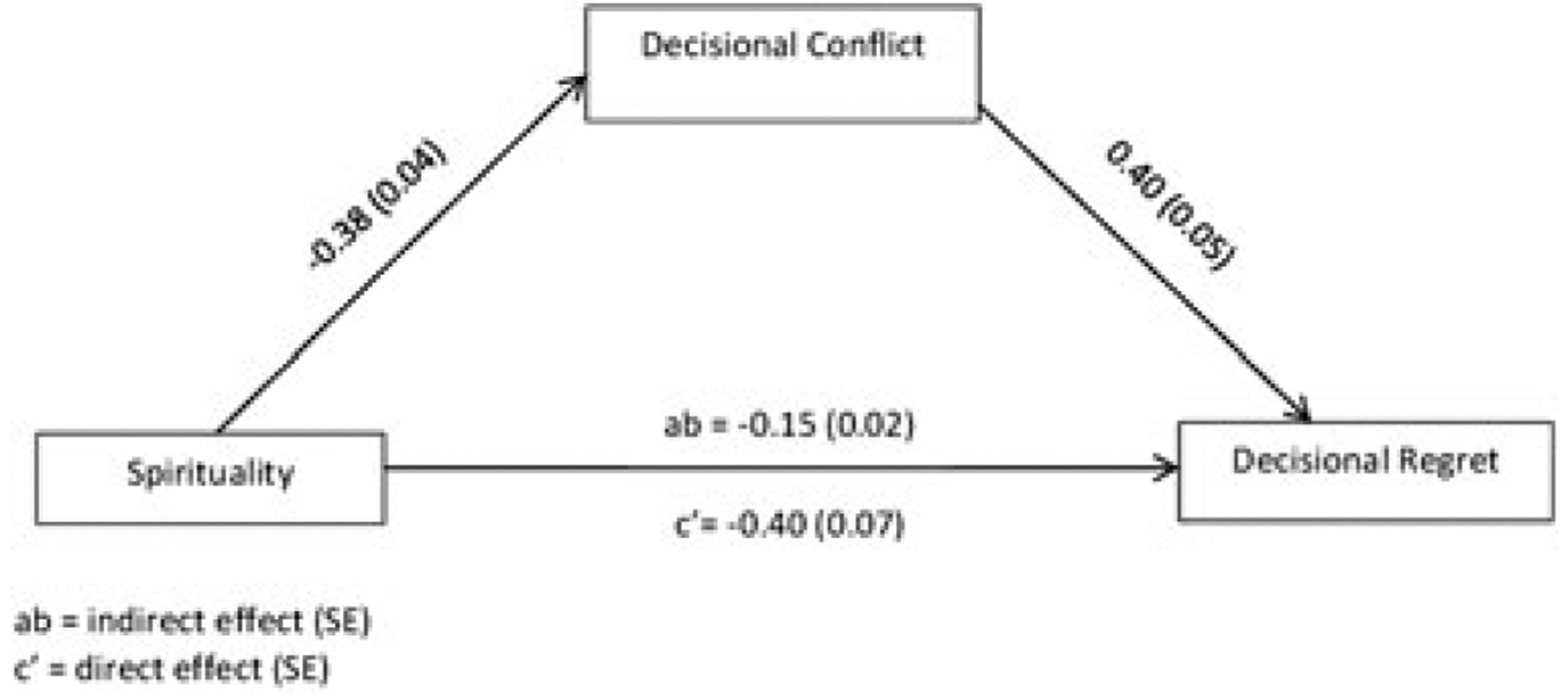
Unstandardized coefficients and associated standard errors for the decisional regret model are presented. In the model, decisional conflict after making treatment decision but before treatment partially mediates the influence of spirituality on decisional regret 6 months after treatment at P < .05. Although not illustrated, demographic and clinical characteristics (Gleason score, education, age at diagnosis, marital status, and race/ethnicity), optimism, and resilience were included in the model as control variables
