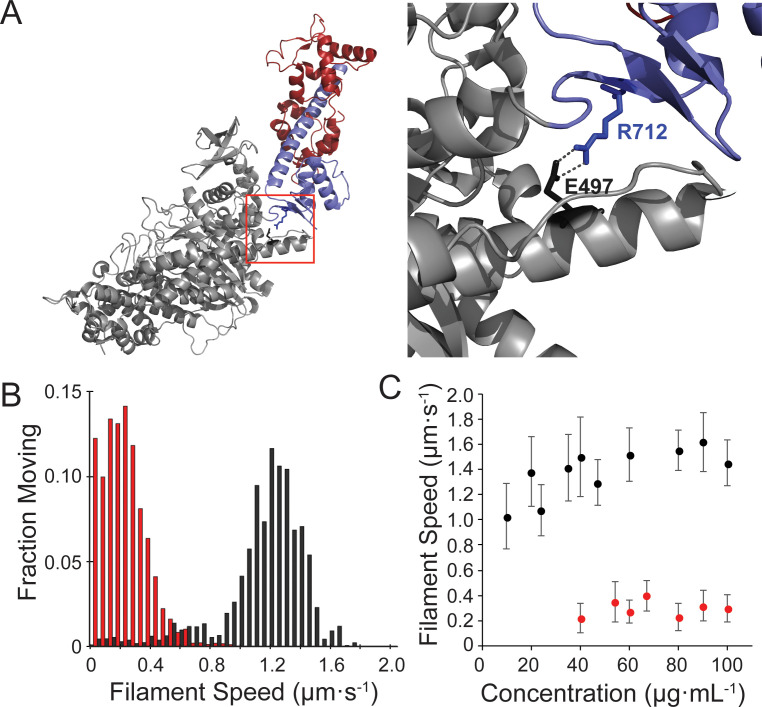
Figure 1. Motility of the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutant, R712L-myosin, is impaired.
(A) Cartoon rendering of the β-cardiac myosin crystal structure (PDB: 5N69). The motor domain (grey, 1–707), converter/lever arm domain (blue, 708–806), and the essential light chain (red) are shown. The box indicates the region expanded to the right showing the E497-R712 salt bridge located at the fulcrum of the lever arm. (B) Distribution of individual filament gliding speeds from motility assays at a concentration of 100 μg⋅ml−1. Wild-type-myosin (black) has a higher average motility rate compared to R712L-myosin (red). (C) Increasing loading concentrations of myosin were added and the average filament speed of fluorescently labelled actin filaments was assessed. Higher concentrations of R712L-myosin were required to achieve motility, and actin filaments were not observed on the surface at concentrations <40 μg⋅ml−1.