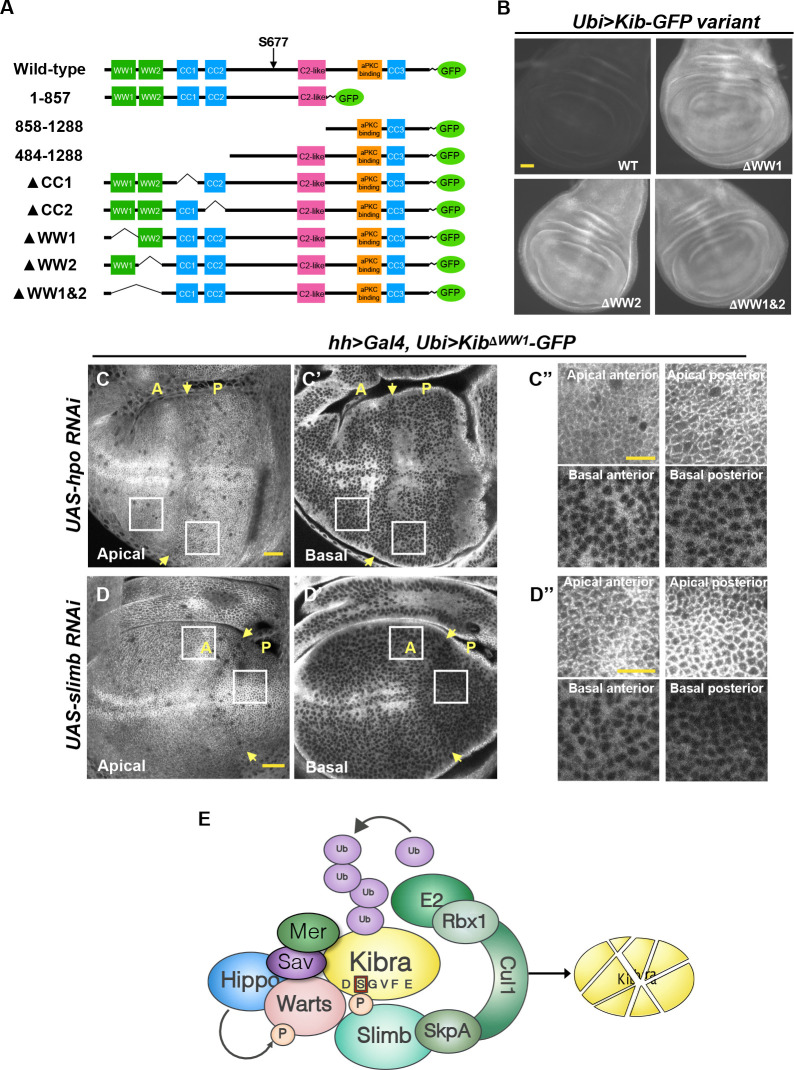
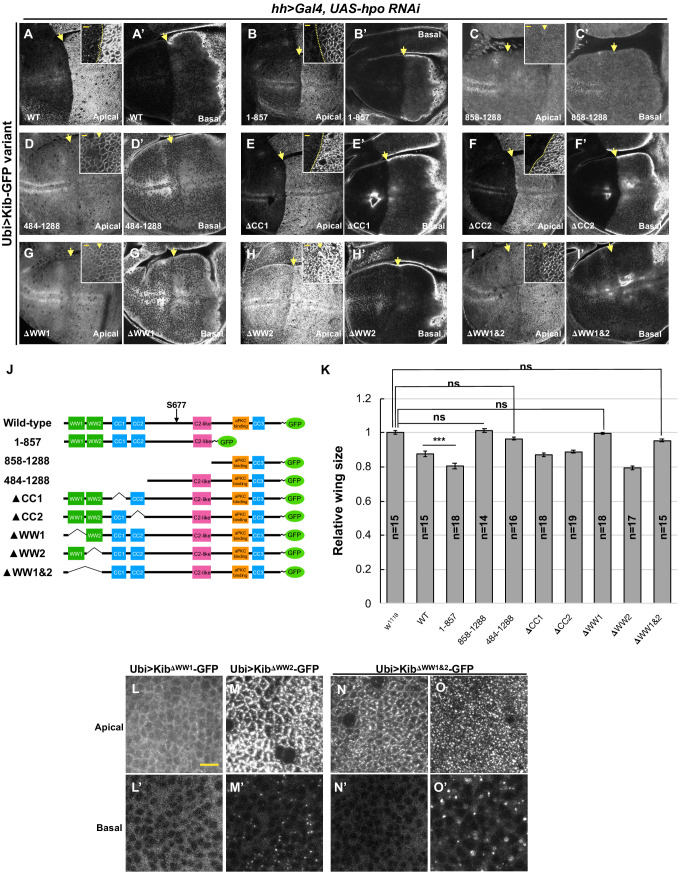
Figure 6. The WW domains of Kibra (Kib) are required for Hippo (Hpo) pathway- and Slimb-mediated degradation.
(A) Diagram of Kib truncations generated for this study. (B) Widefield fluorescence images of wing imaginal discs expressing wild-type and WW-domain truncations of Kib-GFP expressed under the ubiquitin promoter. All images were taken with identical settings. Scale bar=40 μm. (C–C’’) Depletion of Hpo does not affect expression of Ubi>KibΔWW1-GFP. Note that Hpo depletion leads to apical stabilization and basal depletion of KibΔWW1-GFP (C’’). (D–D’’) Depletion of Slimb does not affect expression of Ubi>KibΔWW1-GFP. Note that similar to Hpo depletion, loss of Slimb leads to slight apical stabilization and basal depletion of KibΔWW1-GFP (D’’). Yellow arrows indicate A–P boundary of the wing discs. Scale bars=20 μm (C and D) and 10 μm (C’’ and D’’). (E) A model of Kib degradation by the Hpo pathway and Slimb.