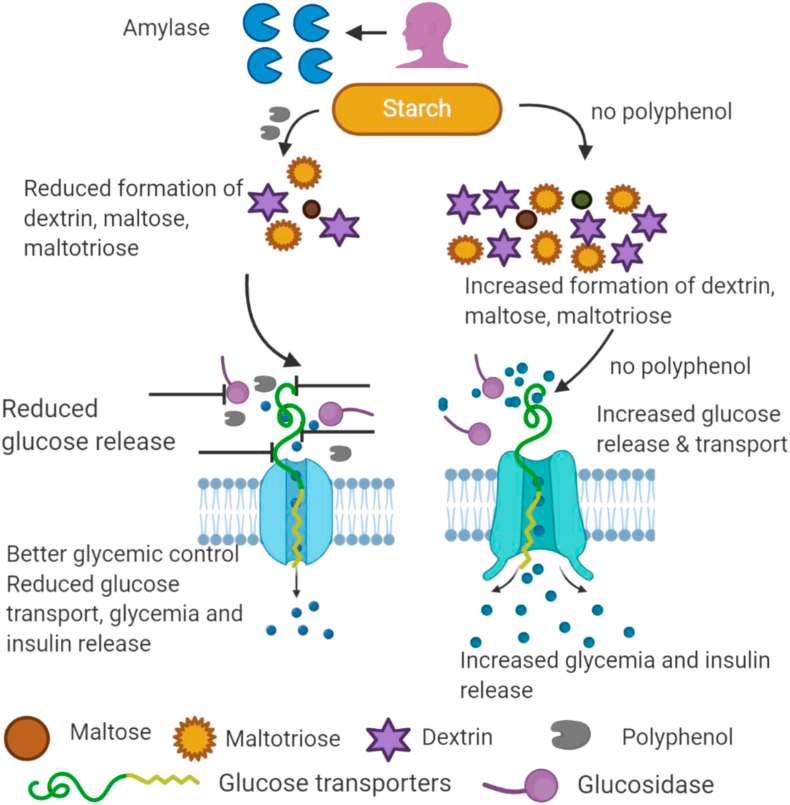
Figure 1.
Plausible mechanisms by which polyphenols inhibit starch digesting enzymes and reduces glucose transport across the epithelia. The left side shows that polyphenols can inhibit amylases leading to reduced formation of maltose, maltotriose, and dextrins. Further, polyphenols also reduce formation and transport of glucose in the brush border membrane by inhibiting glucosidases and glucose transporters. This leads to reduced glycemia and insulin secretion. The right side of the figure shows that when there is no inhibition, there is increased digestion and transport of starch leading to increased glycemia and insulin secretion.