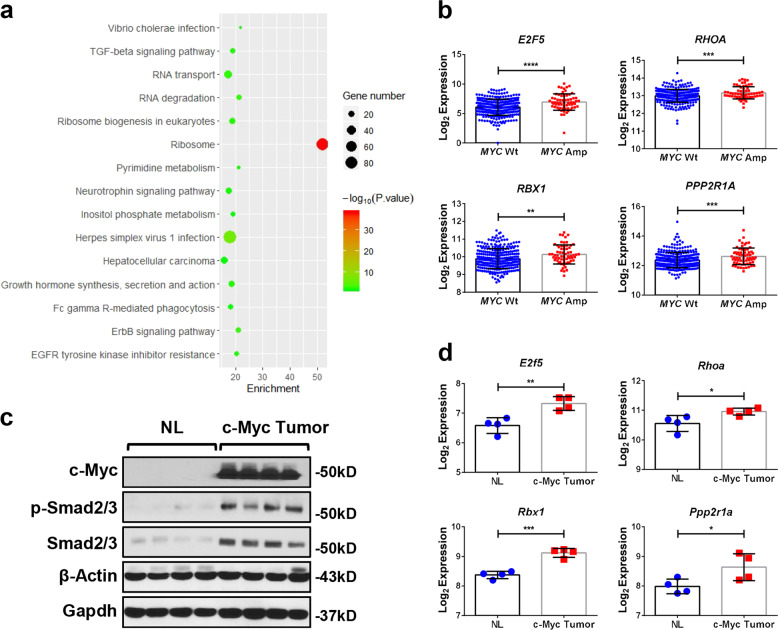
Fig. 1. Genetic crosstalk of c-MYC and TGFβ signaling cascades in human HCCs.
a Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analysis of statistically significant deregulated genes in HCCs harboring c-MYC amplification, showing a significant gene clustering of TGFβ signaling pathway (P = 0.027). b Higher mRNA expression of TGFβ downstream target genes (E2F5, RHOA, RBX1 and PPP2R1A) in c-MYC amplified (MYC Amp; n = 64) HCCs than that in c-MYC non-amplified (MYC Wt; n = 293) HCCs. Student t test was applied for statistical analysis, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. c Western blotting results showing upregulation of p-Smad2/3 in c-Myc murine HCCs (c-Myc Tumor) compared with non-tumorous normal livers (NL). β-Actin and Gapdh were used as loading controls. d Microarray analysis of mRNA expressions of TGFβ downstream target genes (E2f5, Rhoa, Rbx1, and Ppp2r1a) in c-Myc murine HCCs (c-Myc tumor and non-tumorous normal liver, NL). Student t test was applied for statistical analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.