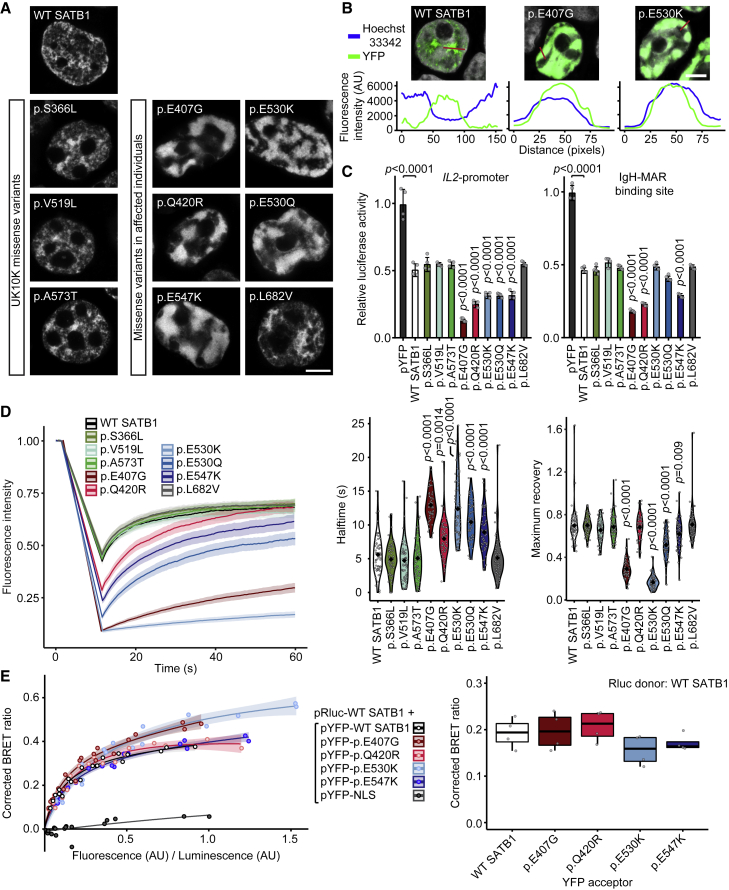
Figure 3.
SATB1 missense variants stabilize DNA binding and show increased transcriptional repression
(A) Direct fluorescence super-resolution imaging of nuclei of HEK293T/17 cells expressing YFP-SATB1 fusion proteins. Scale bar = 5 μm.
(B) Intensity profiles of YFP-tagged SATB1 and variants, and the DNA binding dye Hoechst 33342. The graphs represent the fluorescence intensity values of the position of the red lines drawn in the micrographs on the top (SATB1 proteins in green, Hoechst 33342 in white, scale bar = 5 μm). For each condition a representative image and corresponding intensity profile plot is shown.
(C) Luciferase reporter assays using reporter constructs containing the IL2-promoter region and the IgH matrix associated region (MAR) binding site. UK10K control variants are shaded in green, CUT1 domain variants in red, CUT2 domain variants in blue, and the homeobox variant in gray. Values are expressed relative to the control (pYFP; black) and represent the mean ± SEM (n = 4, p values compared to wildtype SATB1 [WT; white], one-way ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test).
(D) FRAP experiments to assess the dynamics of SATB1 chromatin binding in live cells. Left, mean recovery curves ± 95% C.I. recorded in HEK293T/17 cells expressing YFP-SATB1 fusion proteins. Right, violin plots with median of the halftime (central panel) and maximum recovery values (right panel) based on single-term exponential curve fitting of individual recordings (n = 60 nuclei from three independent experiments, p values compared to WT SATB1, one-way ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test). Color code as in (C).
(E) BRET assays for SATB1 dimerization in live cells. Left, mean BRET saturation curves ± 95% C.I. fitted using a non-linear regression equation assuming a single binding site (y = BRETmax ∗x / (BRET50 / x); GraphPad). The corrected BRET ratio is plotted against the ratio of fluorescence/luminescence (AU) to correct for expression level differences between conditions. Right, corrected BRET ratio values at mean BRET50 level of WT SATB1, based on curve fitting of individual experiments (n = 4, one-way ANOVA and post hoc Bonferroni test, no significant differences). Color code as in (C).
When compared to WT YFP-SATB1 or UK10K variants, most variants identified in affected individuals show a nuclear cage-like localization (A), stronger co-localization with the DNA-binding dye Hoechst 33342 (B), increased transcriptional repression (C), reduced protein mobility (D), and unchanged capacity of interaction with WT SATB1 (E).