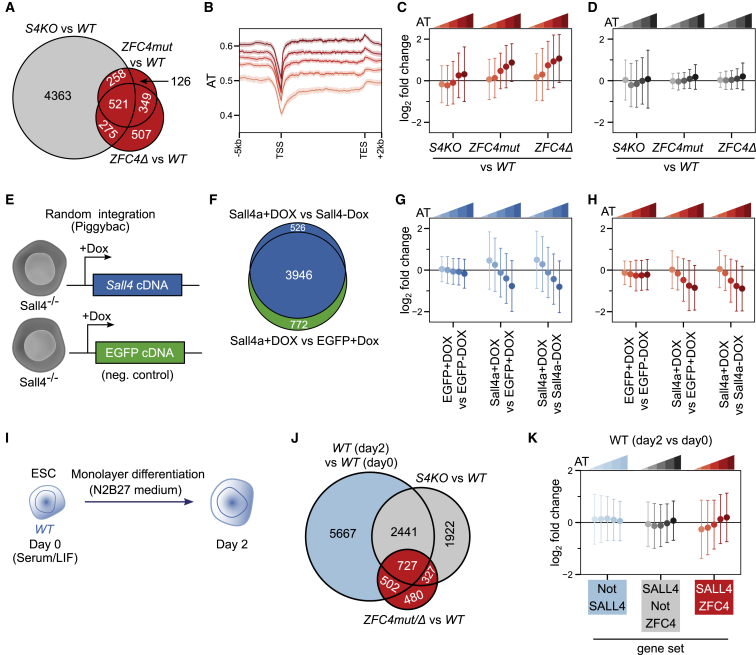
Figure 3.
SALL4-mediated transcriptional regulation in relation to DNA base composition
(A) Venn diagram showing the overlap of differentially expressed genes detected by RNA-seq among S4KO, ZFC4mut, and ZFC4Δ ESCs. ZFC4-regulated genes are indicated in red and ZFC4-independent genes in gray.
(B) Profile plot showing the density of A/T nucleotides around the transcription unit of ZFC4-regulated genes divided into five equal categories according to AT content. TSS, transcription start site; TES, transcription end site.
(C and D) Correlation between gene mis-regulation (log2 fold change versus WT) and DNA base composition in Sall4 mutant ESCs. ZFC4-regulated (C) and ZFC4-independent (D) genes were divided into five equal categories depending on their AT content.
(E) Diagram representing S4KO ESC lines carrying SALL4 or EGFP (control) expression constructs under control of a doxycycline-inducible promoter.
(F) Venn diagram showing the overlap of differentially expressed genes detected by RNA-seq following a 48-h doxycycline induction in the ESC lines presented in (E). SALL4-responsive genes are indicated in blue and EGFP-responsive genes in green.
(G and H) Correlation between SALL4-induced gene expression changes and DNA base composition. SALL4-responsive (G) and ZFC4-regulated (H) genes were divided into five equal categories depending on their AT content, and their relative expression levels were analyzed in the indicated ESC lines.
(I) Diagram showing the protocol used to characterize early differentiation of WT ESCs.
(J) Venn diagram showing the overlap between genes changing during early differentiation of WT cells (day 0 versus day 2) with genes de-regulated in Sall4 mutant ESCs. Genes were divided into three categories: SALL4-independent genes (light blue), SALL4-dependent genes controlled by ZFC4 (red), and SALL4-dependent genes not controlled by ZFC4 (gray).
(K) Correlation between gene expression changes occurring during early differentiation and DNA base composition in WT cells. SALL4-independent genes (light blue), SALL4-dependent genes controlled by ZFC4 (red), and SALL4-dependent genes not controlled by ZFC4 (gray) were divided into five equal categories depending on their AT content, and their relative expression levels were analyzed at day 2 of differentiation.