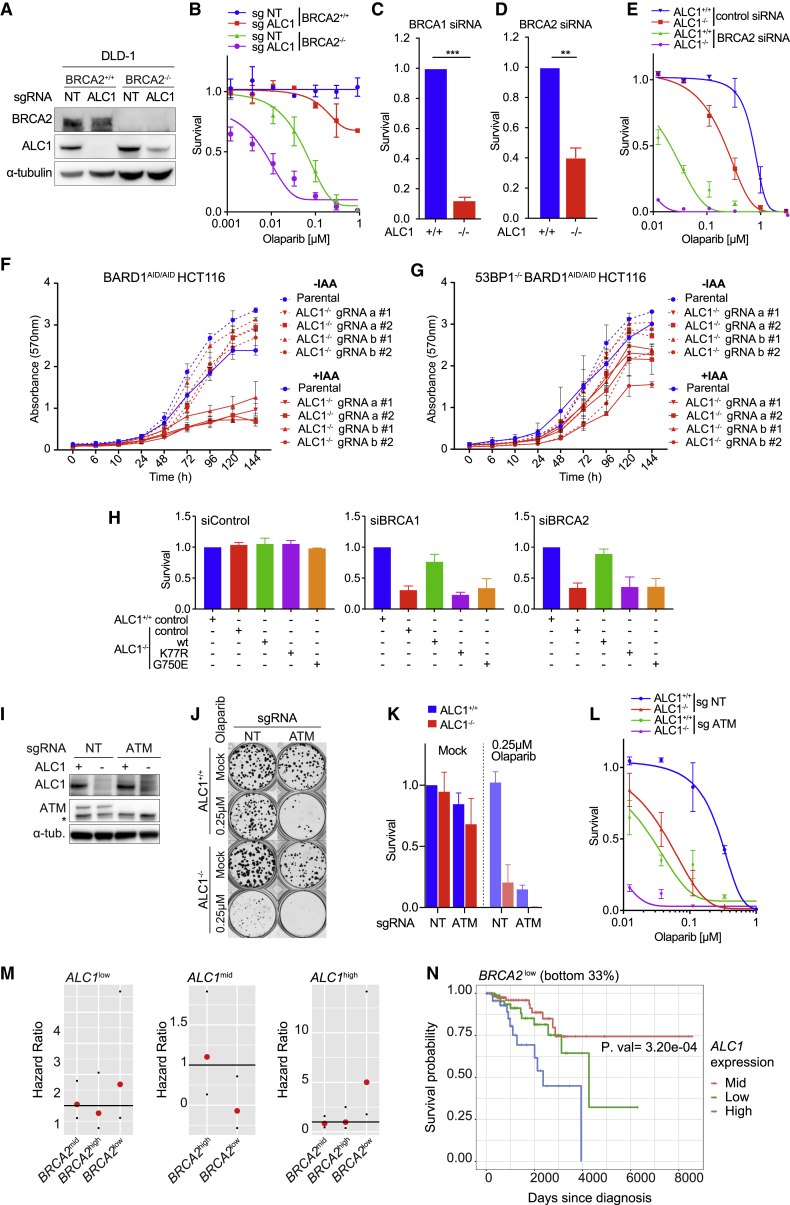
Figure 4.
Defective ALC1-mediated nucleosome remodeling confers synthetic lethality with HRD
(A–E) Loss of ALC1 is synthetic lethal with HRD and leads to PARPi hypersensitivity. (A) Immunoblot of WCEs from DLD-1 WT and BRCA2−/− cells following transduction with LentiCRISPR NT sgRNA and ALC1 sgRNA and clonal selection (no BRCA2/ALC1 double knockouts were recovered), probed with BRCA2 and ALC1. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Olaparib colony survival in DLD-1 BRCA2+/+ALC1+/+, BRCA2−/−ALC1−/−, BRCA2−/−ALC1+/+, and BRCA2−/−ALC1Low expression. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to untreated cells (n = 3 independent biological experiments). Solid lines show a nonlinear least-squares fit to a four-parameter dose-response model. (C) Survival in ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− eHAP cells transfected with BRCA1-targeting short interfering RNAs (siRNAs). Cell survival was measured using CellTiter-Glo. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to ALC1+/+ cells (n = 3 independent biological experiments). (D) Survival in ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− eHAP cells transfected with BRCA2-targeting siRNAs. Cell survival was measured using CellTiter-Glo. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to ALC1+/+ cells (n = 3 independent biological experiments). (E) Olaparib survival in ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− eHAP transfected with non-targeting or BRCA2-targeting siRNAs. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to untreated cells (n = 3 independent biological experiments). Solid lines show a nonlinear least-squares fit to a four-parameter dose-response model.
(F) Quantification of a crystal violet proliferation assay in parental and ALC1-deleted BARD1AID/AID cells ± IAA. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent biological experiments).
(G) Quantification of a crystal violet proliferation assay in parental and ALC1-deleted 53BP1−/−BARD1AID/AID cells ± IAA. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 independent biological experiments).
(H) ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− eHAP cells transduced with indicated ALC1 constructs were transfected with non-targeting, BRCA1-targeting, or BRCA2-targeting siRNAs. Cell survival was measured using CellTiter-Glo. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to ALC1+/+ cells for each siRNA (n = 3 independent biological experiments).
(I) Immunoblot of WCEs in ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− iCAS9 eHAP cells transduced with ATM sgRNA following 72 h Dox, probed with antibodies against ALC1 and ATM. α-tubulin is used as a loading control.
(J) Representative images (n = 3 biologically independent experiments) of clonogenic survival assays in ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− iCAS9 cells expressing NT and ATM sgRNA following 72 h Dox ± 250 nM Olaparib.
(K) Quantification of clonogenic survival assays in ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− iCAS9 cells expressing NT sgRNA and ATM sgRNA following 72 h Dox ± 250 nM Olaparib. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to non-treated ALC1+/+ NT sgRNA (n = 3 biologically independent experiments).
(L) Olaparib survival of ALC1+/+ and ALC1−/− iCAS9 cells transduced with NT sgRNA and ATM sgRNA following 72 h Dox. Data are mean ± SEM normalized to untreated cells (n = 3 independent biological experiments). Solid lines show a nonlinear least-squares fit to a four-parameter dose-response model.
(M) Hazard ratio analysis of breast cancer patients from TGCA according to ALC1 and BRCA2 expression.
(N) KM survival analysis of BRCA2low breast cancer patients from TGCA according to ALC1 expression. ns, p > 0.05; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.