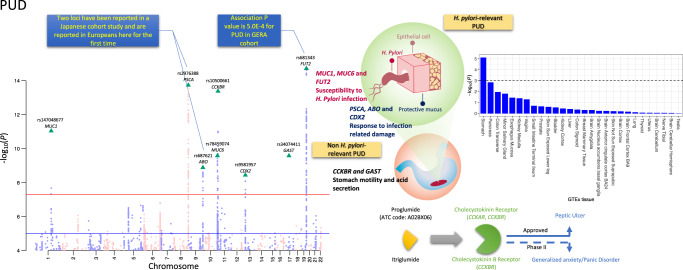
Fig. 2. Manhattan plot of peptic ulcer disease (PUD) for SNPs associated P < 1.0E−4 from BOLT-LMM association test.
SNPs highlighted with green triangles are independent loci with P < 5.0E−8. rs2976388 and rs687621 are the only two loci associated with duodenal ulcer in a Japanese cohort18 and rs681343 showed statistically significant association in GERA PUD GWAS, as annotated in the blue box. SNPs on odd/even chromosomes are presented in mauve/pink. Schematic diagram on the right side represents the reported biological evidence supporting involvement in peptic ulcers of genes physically located near PUD-associated loci (noting that we do not have direct evidence to link the associated SNPs with the genes). MUC176, MUC677, and FUT273 have been linked to susceptibility to H. pylori infection and PSCA and ABO have been proposed to be associated with subsequent response after infection18. Induced/enhanced CDX2 expression as a result of H. pylori infection of gastric epithelial cell lines has been observed79. GAST encodes gastrin, which is a hormone whose main function is to stimulate secretion of hydrochloric acid by the gastric mucosa. CCKBR encodes cholecystokinin receptor which mediates a therapeutic effect for peptic ulcer treatment by reducing acid secretion and inhibiting gastrointestinal motility. The cholecystokinin receptor is also an effect-mediating target of itriglumide on phase II clinical trial for anxiety and panic disorder81. Using the GENE2FUNC of FUMA pipeline38, we found that the eight annotated genes are highly overexpressed in human stomach tissue from GTEx 8th version data, as shown in the bar plot on the right side with data presented in Supplementary Data 2. The dashed line represents Bonferroni corrected significance at −log10(0.05/54).