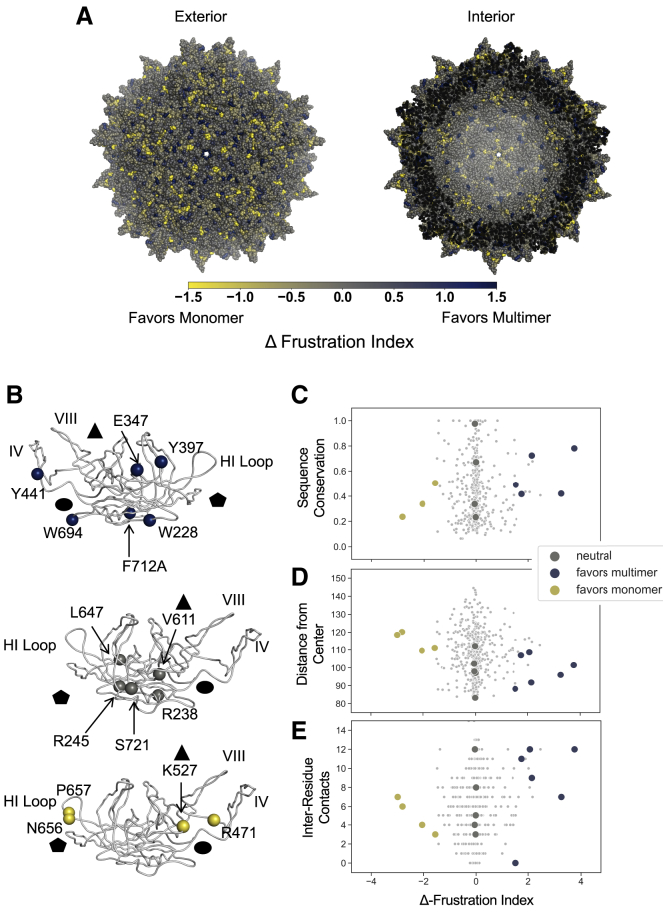
Figure 2.
AAV2 Δ-frustration index and capsid residues selected for experimental analysis. AAV2 Δ-frustration index was computed as the difference between monomer and multimer single-residue frustration indices. Residues with a positive Δ-frustration index are predicted to favor the multimer, whereas residues with a negative Δ-frustration index are predicted to favor the monomer. (A) AAV2 60-mer capsid crystal structure colored according to Δ-frustration index is given. Views of the capsid from exterior and interior are shown. (B) Residues selected for experimental analysis are shown. Residues favoring the multimer state (blue, Δ-frustration index >1.5), residues favoring the monomer state (yellow, Δ-frustration index <−1.5), and neutral residues (gray, Δ-frustration index >−0.1 and <0.1) were selected for further study. The capsid fivefold (pentagon), threefold (triangle), and twofold (circle) axes of symmetry are indicated. Top view shows interior face of the VP3 subunit, and middle and bottom views show exterior face. Δ-frustration index for AAV2 capsid residues was plotted against (C) sequence conservation in the parvovirus family computed using Shannon entropy of reweighted sequences normalized from 0 to 1 (1 indicates full conservation), (D) residue distance from center of AAV2 capsid (Å), and (E) number of residue-residue contacts according to a 4.5 Å heavy-atom distance threshold. Residues selected for mutation are large colored circles, and residues not selected are small gray dots.