Figure 4.
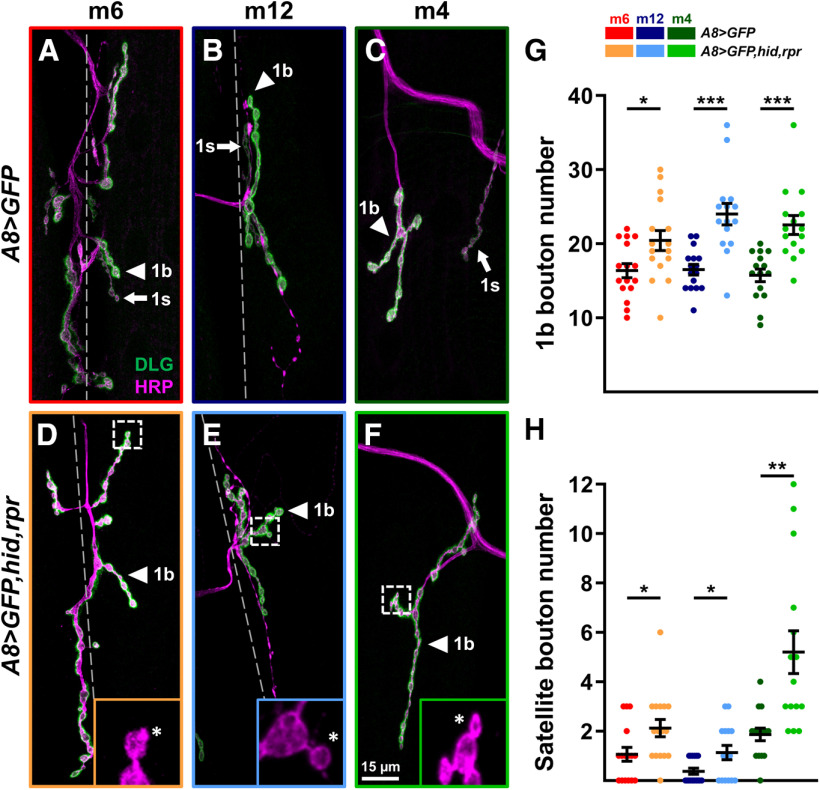
1b NMJs expand upon ablation of 1s MNs. A–F, Representative NMJ arbors (1b arbors and 1s arbors, arrowheads and arrows, respectively) of m6 (A, D), m12 (B, E), and m4 (C, F) labeled with DLG (green) and HRP (magenta) in control (A8>GFP) and 1s-ablated (A8>GFP,hid,rpr) third instar larvae. Insets are 5× zoomed images of corresponding dashed regions in D–F. Satellite boutons are indicated by asterisks. Note that 1s NMJs are absent in 1s-ablated animals. Images and graphs are color coded as indicated in the color key. G, Quantification of 1b bouton number of m6 (t(30)=2.458, p = 0.02, unpaired t test), m12 (t(26)=4.449, p = 0.0001, unpaired t test), and m4 (t(28)=4.431, p = 0.0001, unpaired t test) in control and 1s-ablated animals (satellite 1b boutons were not included). H, Quantification of satellite boutons of m6 (t(30)=2.359, p = 0.025, unpaired t test), m12 (t(19.05)=2.397, p = 0.0269, unpaired t test with Welch's correction), and m4 (t(16.41)=3.682, p = 0.0019, unpaired t test with Welch's correction) in control and 1s-ablated animals. Error bars indicate ±SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. n values (NMJs/larva) are 16/8, 16/8, 16/8, 15/8, 15/8, and 15/8, respectively.