Figure 6.
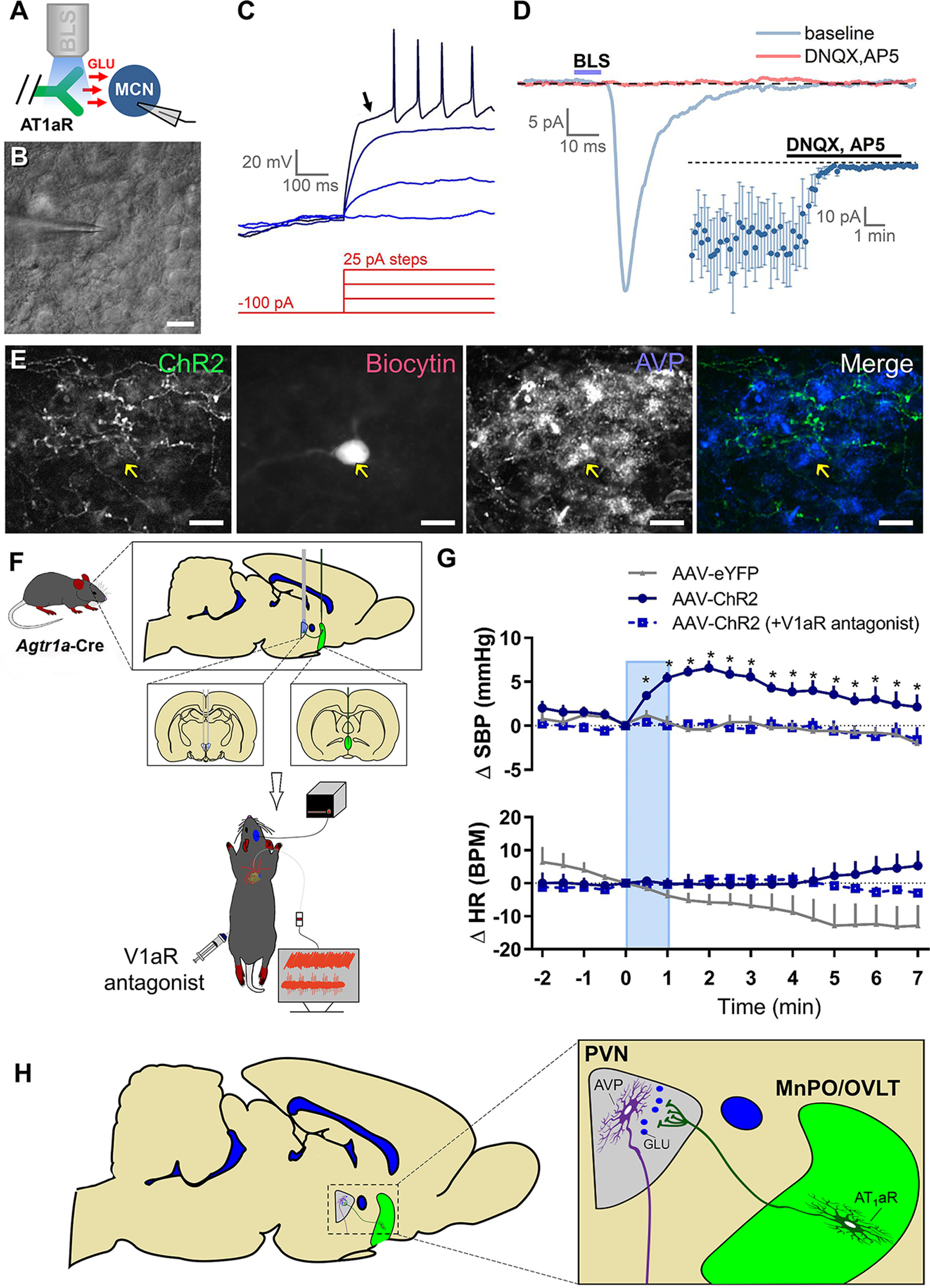
Optogenetic stimulation of axons in the PVN that originate from MnPO/OVLT AT1aR neurons releases glutamate (GLU) onto magnocellular (MCN) PVN neurons and induces a V1aR-dependent elevation in blood pressure. A, Experimental design for in vitro optogenetic study. B, PVN magnocellular neurons were initially targeted based on their location, large soma, and general morphology as apparent under IR-DIC. C, Classification as a PVN magnocellular neuron was confirmed during current-clamp recordings based on the presence of a large IA current. This current is responsible for the long delay to first action potential observed in response to suprathreshold stimulation following a brief hyperpolarizing step (arrow). D, Blue light stimulation (BLS) evoked EPSCs in 15 of 65 magnocellular neurons tested. A subset of light-evoked responses observed (5 of 15) were challenged with ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists (DNQX and AP5), which effectively eliminated the response (inset). E, Post hoc immunohistochemical assessment of a light-responsive PVN magnocellular neuron suggests an AVP phenotype. F, Schematic depicting the experimental design used to determine the role of V1aR in cardiovascular responses to blue light stimulation of afferents arising from AT1aR-containing neurons of the MnPO/OVLT. For these studies, the AAV-ChR2 or AAV-eYFP was injected into the MnPO/OVLT of Agtr1a-Cre mice and the fiber-optic post was positioned over the PVN. G, SBP (top) and HR (bottom) response to blue light stimulation of axons in the PVN arising from MnPO/OVLT AT1aR-expressing neurons (10 mW; 15 Hz; 60 s). n = 4 or 5/group. H, Illustration of the overall conclusion that AT1aR neurons in the MnPO/OVLT elicits elevations in blood pressure, in part, via excitatory connections to neurons in the PVN that secrete AVP into the systemic circulation. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05. Scale bars, 20 µm.
