Figure 1.
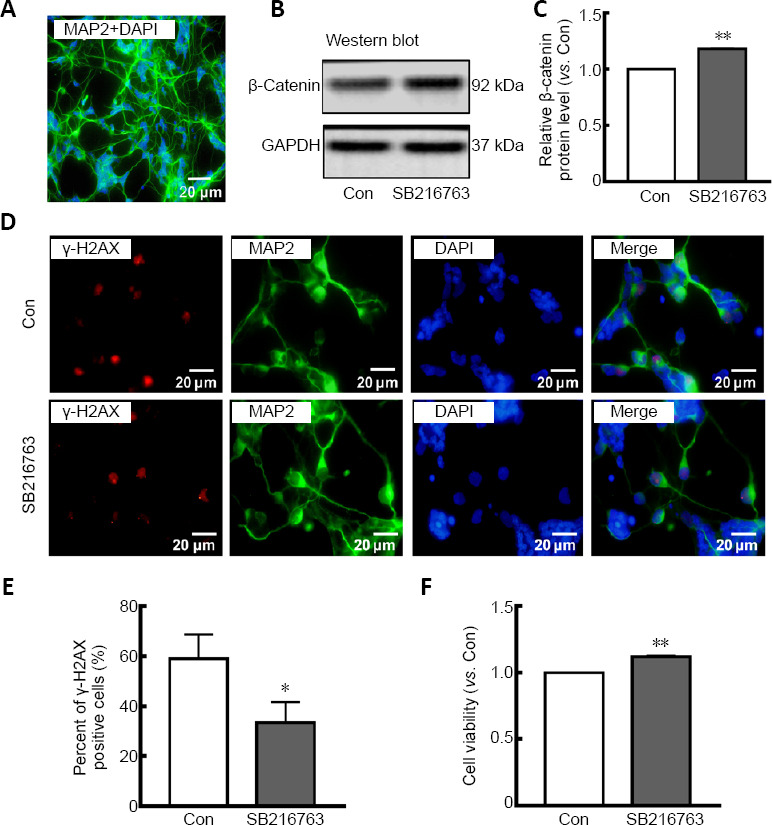
SB216763 suppresses DNA damage and increases cell viability in serum-deprived retinal neurons.
(A) Retinal neurons were cultured and stained for MAP2 (Alexa Fluor 488, green), and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) SB216763 upregulated expression of β-catenin, the substrate of GSK-3β. (C) Relative protein expression of β-catenin is presented as a histogram. (D) Double staining for MAP2 (green staining by Alexa Fluor 488) and γ-H2AX (red staining by Alexa Fluor 555) in serum-deprived retinal neurons. SB216763 significantly inhibited γ-H2AX foci formation in serum-deprived retinal neurons. (E) Relative quantification of γ-H2AX expression was determined by counting foci in 50 randomly selected MAP2-positive cells. Scale bars: 20 μm. (F) SB216763 treatment improved cell viability in serum-deprived retinal neurons, as evidenced by a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. n = 3 for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. control (Con) group (Student’s t-test). DAPI: 4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole; Gapdh: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GSK-3β: glycogen synthase kinase-3β; MAP2: microtubule-associated protein-2; SB216763: a GSK-3β inhibitor; γ-H2AX: γ-H2A histone family member X.
