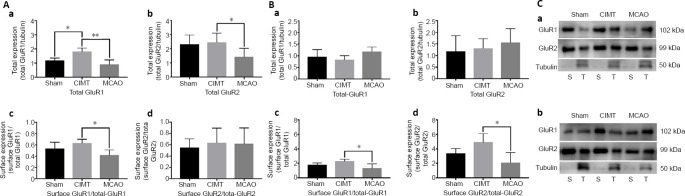
Figure 4.
CIMT increases total synaptic and surface AMPAR expression in the ipsilateral hemisphere.
(A) In the ipsilateral sensorimotor cortex, total synaptic GluR1 and GluR2 (a, b) and surface GluR1 (c) expression was higher in the CIMT group than in the MCAO group; surface expression of GluR2 was increased in the CIMT group, but this was non-significant (d). (B) In the ipsilateral hippocampus, total synaptic GluR1 and GluR2 levels did not differ between groups (a, b). However, surface GluR1 and GluR2 levels were higher in the CIMT group than in the MCAO group (c, d). (C) Tubulin, which is not present in the membrane fraction, served as a reference to test the purity of the extracted membrane proteins. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). AMPAR: a-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor; CIMT: constraint-induced movement therapy; GluR: glutamate receptor; MCAO: middle cerebral artery occlusion; S: membrane surface protein; T: synaptic total protein.