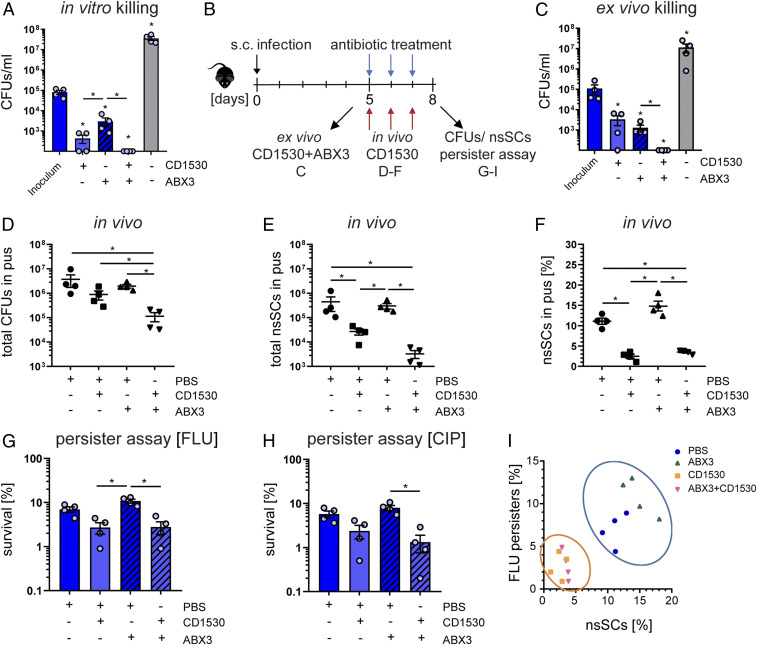
Fig. 6.
S. aureus persister levels are reduced in the presence of retinoid derivatives during antibiotic treatment. (A) In vitro killing of pH 5.5-stressed bacteria using the retinoid derivative CD1530 (20 µg/mL), ABX3 (40× MIC) alone, or CD1530 together with ABX3. Bacterial survival was assessed after 24 h. N = 4. (B) Overview of the murine abscess model. (C) Ex vivo killing assay of bacteria harvested from murine abscesses using the retinoid derivative CD1530 (20 µg/mL) alone, ABX3 (40× MIC), or CD1530 together with ABX3. Bacterial survival was assessed after 24 h. Bacteria from four independent mice were used. (D) Total CFU counts in mouse abscess pus at day 8. N = 4. (E) Total nsSCs counts in mouse abscess pus at day 8. (F) Percentage of nsSCs in mouse abscess pus at day 8. N = 4. (G) Ex vivo antibiotic challenge with FLU (40× MIC) for 24 h. Bacterial survival was determined relative to the inoculum. Bacteria from four independent mice were used. (H) Ex vivo antibiotic challenge with CIP (40× MIC) for 24 h. Bacterial survival was determined relative to the inoculum. (I) Correlation between the proportion of nsSCs and the proportion of persisters (FLU). CD1530 exposure reduced both nsSCs and persisters (FLU challenge). Each symbol represents one biological replicate. *P < 0.05; Error bars depict SEM.