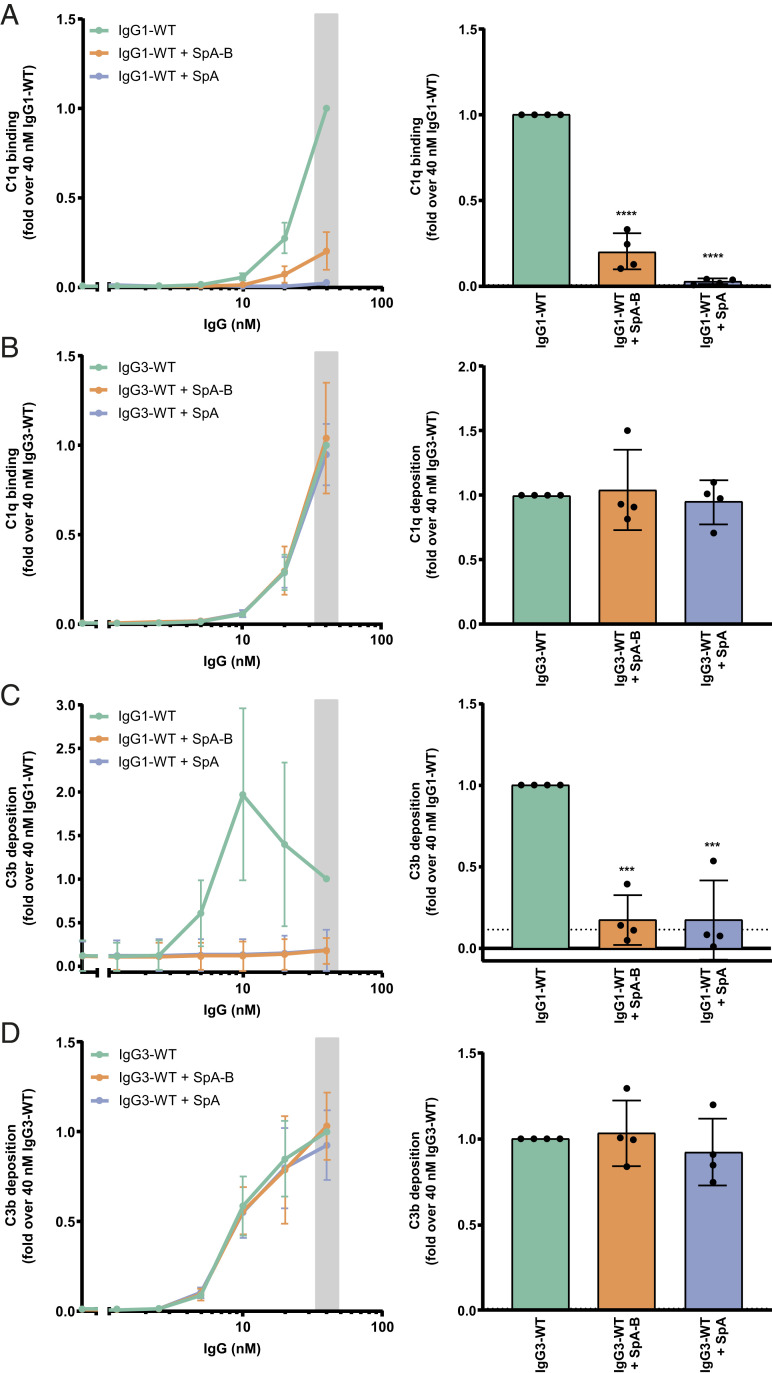
Fig. 6.
SpA decreases IgG-mediated C1q binding and downstream complement on S. aureus. (A and B) C1q binding on anti-WTA wild-type IgG1 (IgG1-WT) (A) or IgG3 antibodies (IgG3-WT) (B) bound to the NewmanΔspa/sbi surface after incubation of bacteria with 1% ΔIgG/IgM human serum in the absence (green) or presence of SpA-B (orange) or SpA (blue), detected with a chicken anti-human C1qA antibody by flow cytometry. (C and D) C3b deposition on the NewmanΔspa/sbi surface after incubation of bacteria with IgG1-WT (C) or IgG3-WT (D), 1% ΔIgG/IgM human serum and buffer (green), and SpA-B (orange) or SpA (blue), detected with a monoclonal murine anti-human C3d antibody by flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± SD fold change over 40 nM concentration of IgG control of at least three independent experiments. Bars represent the same data for the 40 nM IgG concentration only, and the black dotted line shows the background fluorescence from bacteria not incubated with IgG. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA to compare buffer condition with SpA-B and SpA conditions. ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.