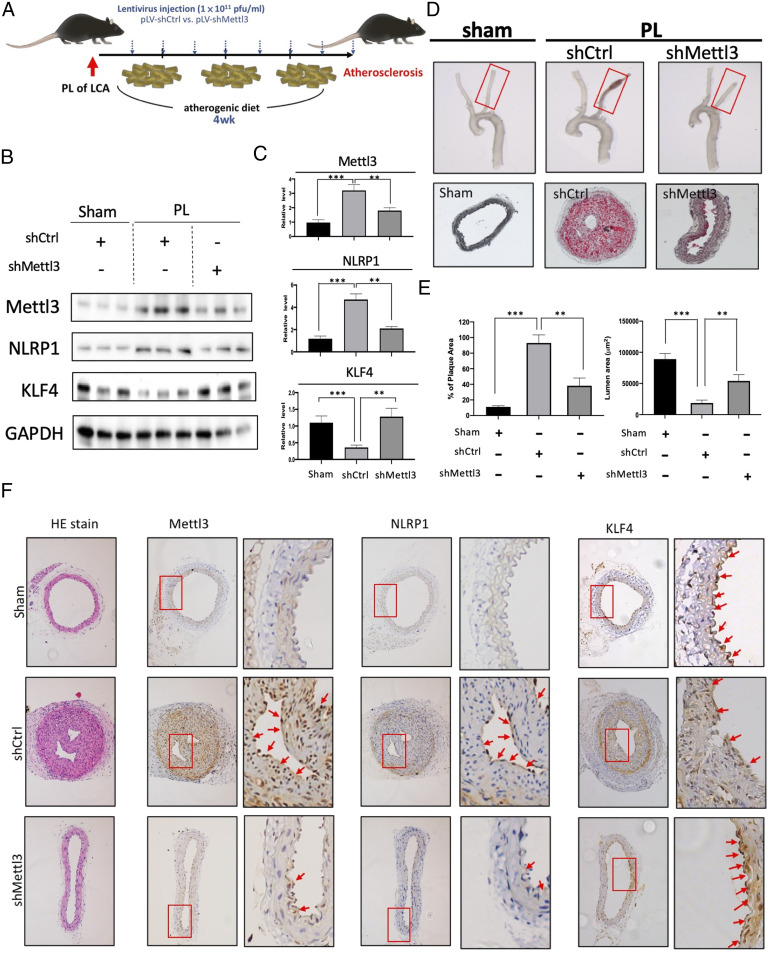
Fig. 5.
Mettl3 knockdown inhibits atherogenesis in vivo. (A) The experimental design for Mettl3 gene knockdown expression in the partial ligation (PL)-induced high-cholesterol atherogenic diet-fed ApoE−/− mouse model of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerotic lesions were induced by PL over 4 wk. Lentivirus encoding control shRNA (pLV-shCtrl) or shRNA targeting Mettl3 (pLV-shMettl3) was repetitively administered twice per week. (B) Western blot and its quantification (C) showing the expression of METTL3, NLRP1, and KLF4 proteins in the arterial endothelium from mice with indicated treatments. (D) Gross necropsy (Upper) of LCAs from ApoE−/− mice with indicated treatments. Plaque formation and the changes in lumen size (Center) were evaluated using Oil Red O staining. (E) The formation of Oil Red O-stained plaques and quantitation of lumen area. (F) Hematoxylin and eosin staining and immunohistochemistry analysis of METTL3 and NLRP1 proteins in the cross-sections from sham-operated LCA and PL LCA with indicated treatments. Boxes highlighted the expression patterns of METTL3, NLRP1, and KLF4 in the endothelium from LCA.