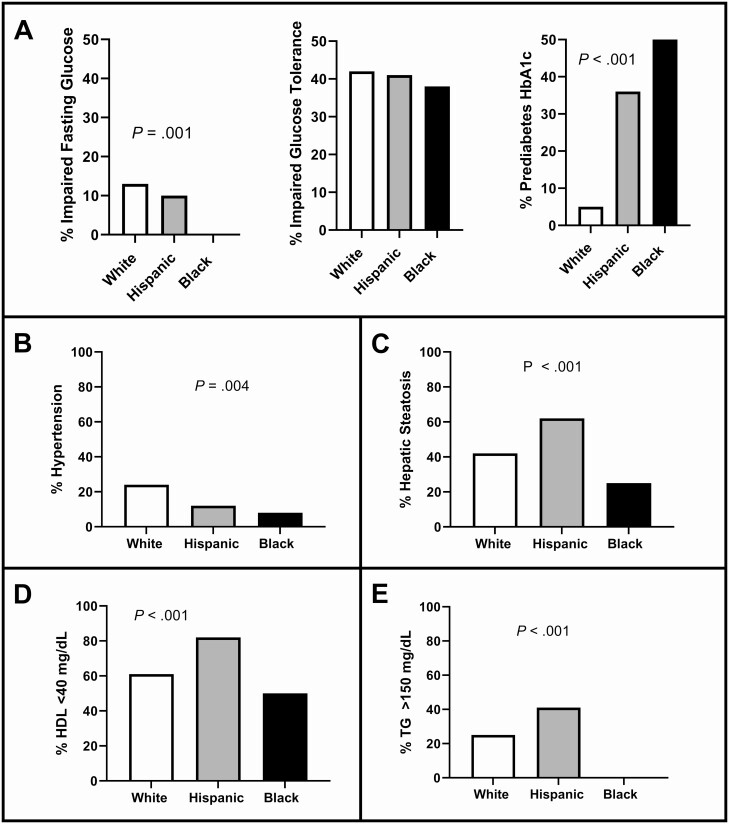
Figure 2.
Proportions of metabolic syndrome. Data are presented comparing the 3 groups of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (white, Hispanic, and black) as percentages graphed as a column bar graph. Because these are percentages, there are no SE bars. Statistical analyses were performed using ordinary analysis of variance tests where significance was P less than .05. According to the American Diabetes Association, a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome requires displaying 3 of the 5 following criteria: 1) dysglycemia measured by fasting glucose greater than or equal to 100 mg/dL (impaired fasting glucose), 2-hour glucose levels of 140 to 199 mg/dL (range, 7.8-11.0 mmol) on the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (impaired glucose tolerance), and/or elevated glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of 5.7% to 6.4% (prediabetes HbA1c); 2) blood pressure greater than or equal to 130/85 mm Hg or being treated for high blood pressure (hypertension); 3) liver fat greater than 5% (hepatic steatosis has been included in place of waist circumference because a standard waist circumference by race has yet to be fully determined); 4) high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol less than 40 mg/dL; and 5) triglycerides (TG) greater than or equal to 150 mg/dL.