Figure 1. Receptors binding GDF-15:
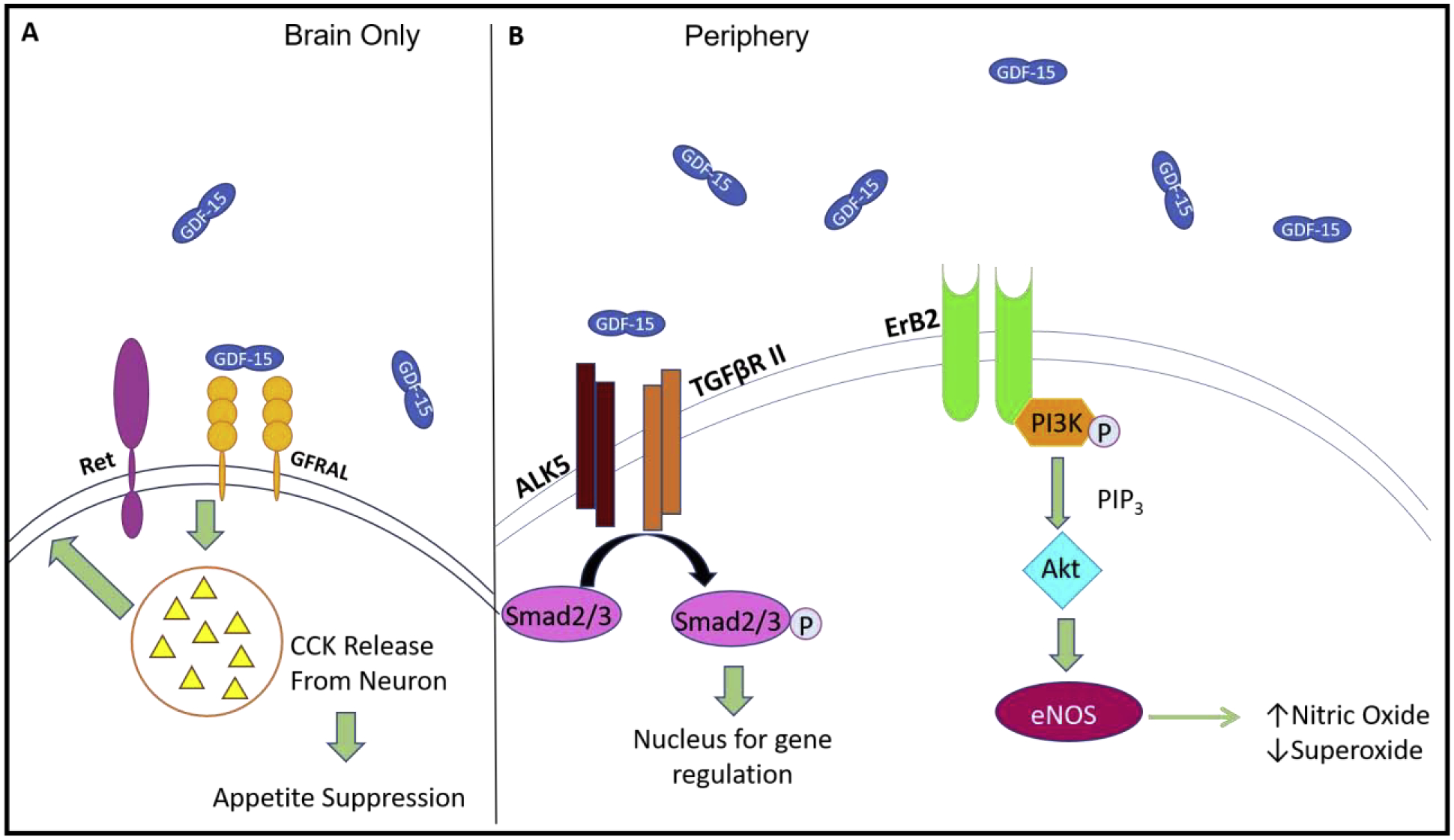
In the brain, GDF-15 binds GFRAL and interacts with the co-receptor Ret. Binding of GDF-15 to the receptor in the brain ultimately leads to release of neurotransmitter CCK, which works to suppress appetite (A). Throughout the rest of the body, GDF-15 is able to bind several other receptors including TGF-βRs and ALKs. Binding of these receptor combinations leads to activation of Smad2/3, ultimately leading to changes in gene expression (ie decrease in NF-κB expression). GDF-15 also binds endothelial receptor Erb2. Activation of Erb2 leads to activation of the PI3K and Akt pathways, ultimately resulting in upregulation of eNOS (B).
