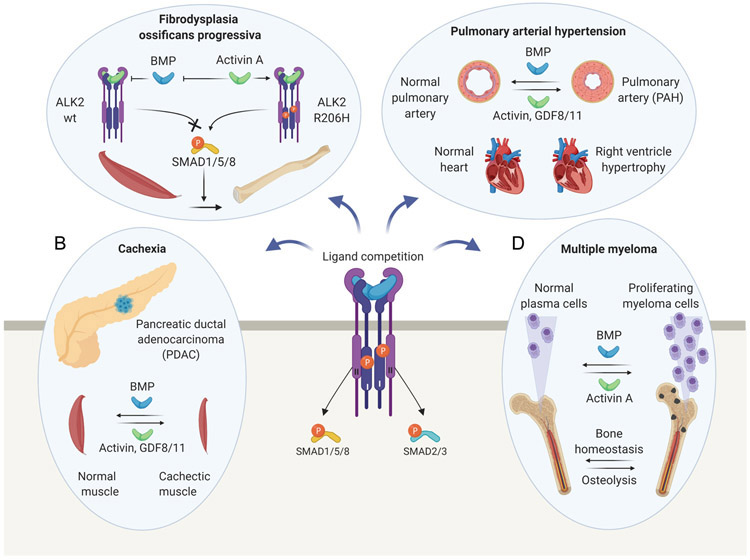
Figure 6. Proposed pathological roles of ligand competition.
A. Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP). In wild-type cells, activin A antagonizes BMP signaling by forming an inhibitory, non-signaling complex with ALK2 and type II receptors. In FOP, disease-causing ALK2 variants perceive activin A as an agonist that aberrantly activates the SMAD1/5/8 pathway, and, thus, induces osteogenic differentiation of fibroadipogenic progenitors to form ectopic bone. B. Wasting Syndrome/Cachexia. BMP signaling is vital for muscle and adipose tissue formation and maintenance. Elevated activin/GDF levels in patients with pancreatic cancers may antagonize BMP-SMAD1/5/8 activity in these tissues, contributing to cancer cachexia. C. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH). Deficient BMP-SMAD1/5/8 and increased activin-SMAD2/3 signaling may contribute to endothelial arterial cell proliferation in PAH patients, and, thus, to the narrowing of pulmonary arteries. Increased activin/GDF-11 levels could promote PAH by shifting the balance from SMAD1/5/8 to SMAD2/3 signaling. D. Multiple Myeloma (MM). BMP signaling helps maintain MM cells in a slow-proliferating state. Activin A expression is induced in the bone marrow of MM patients and may contribute to tumor cell expansion by antagonizing BMP activity. Also, activin A may alter bone homeostasis and contribute to MM bone disease by suppressing osteoblastic bone formation and inducing osteoclastic bone destruction.