Fig. 7. Chronic Notch inhibition in carcinogen-treated mice leads to β-catenin-dependent HCC.
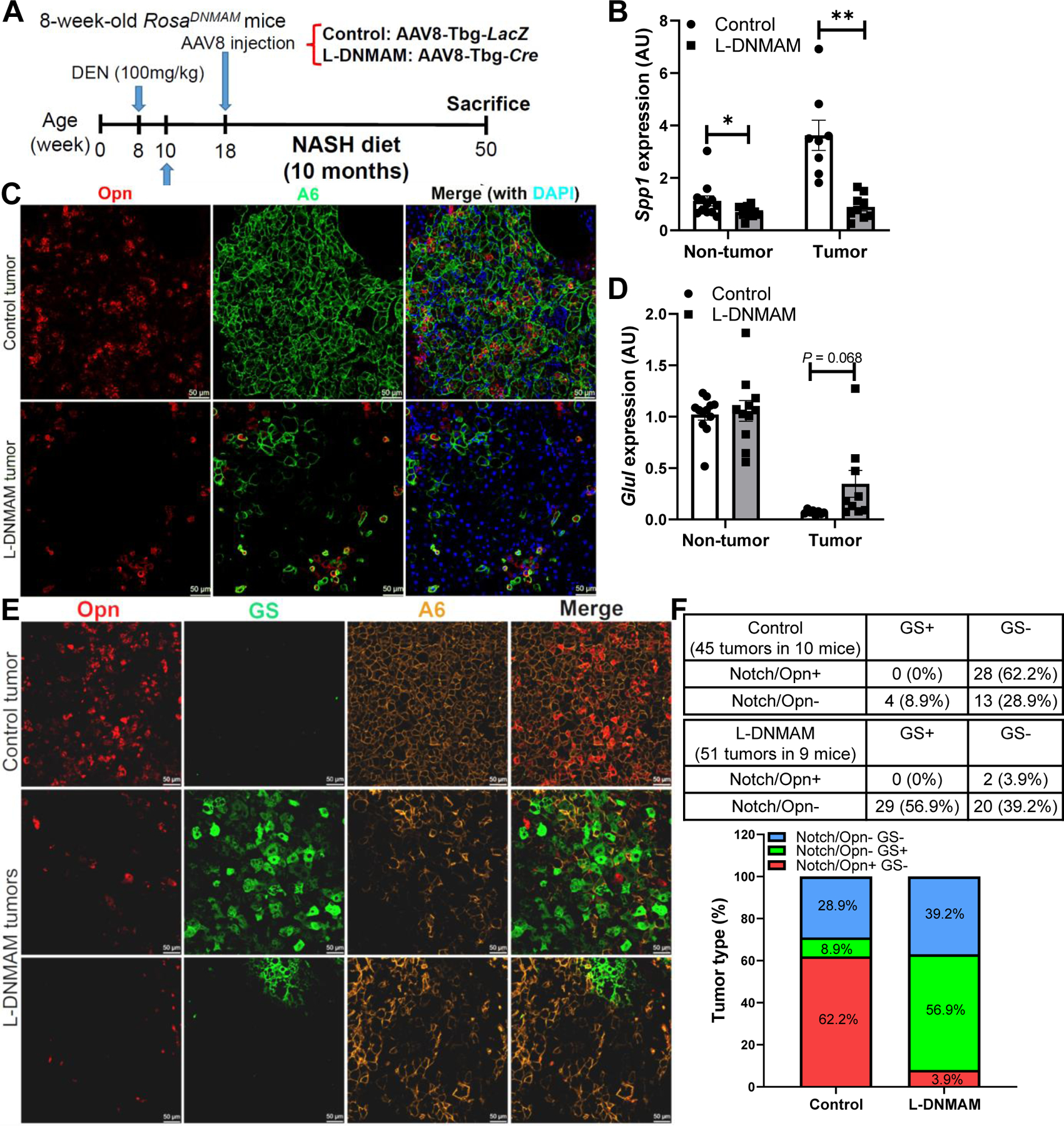
(A) RosaDNMAM mice were dosed with DEN (100 mg/kg), fed NASH diet, then transduced with AAV8-Tbg-LacZ (control) or AAV8-Tbg-Cre (L-DNMAM) (n = 9–10 per group). (B) L-DNMAM tumors show reduced expression of the Notch target Spp1, (C) with correspondingly lower tumor co-staining of Opn (red). (D) L-DNMAM tumors show increased tumoral expression of the β-catenin target Glul, (E) with correspondingly increased tumor co-staining with GS (green). (F) Quantification of Notch/Opn+ and GS+ tumors. *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 as compared to the indicated control by two-tailed t tests. AU, arbitrary unit. Data are shown as means ± SEM.
