Fig. 2. Knockdown of ANT3 or CypD attenuates mortalin depletion-induced lethality in vemurafenib-resistant B-RafV600E melanoma cells.
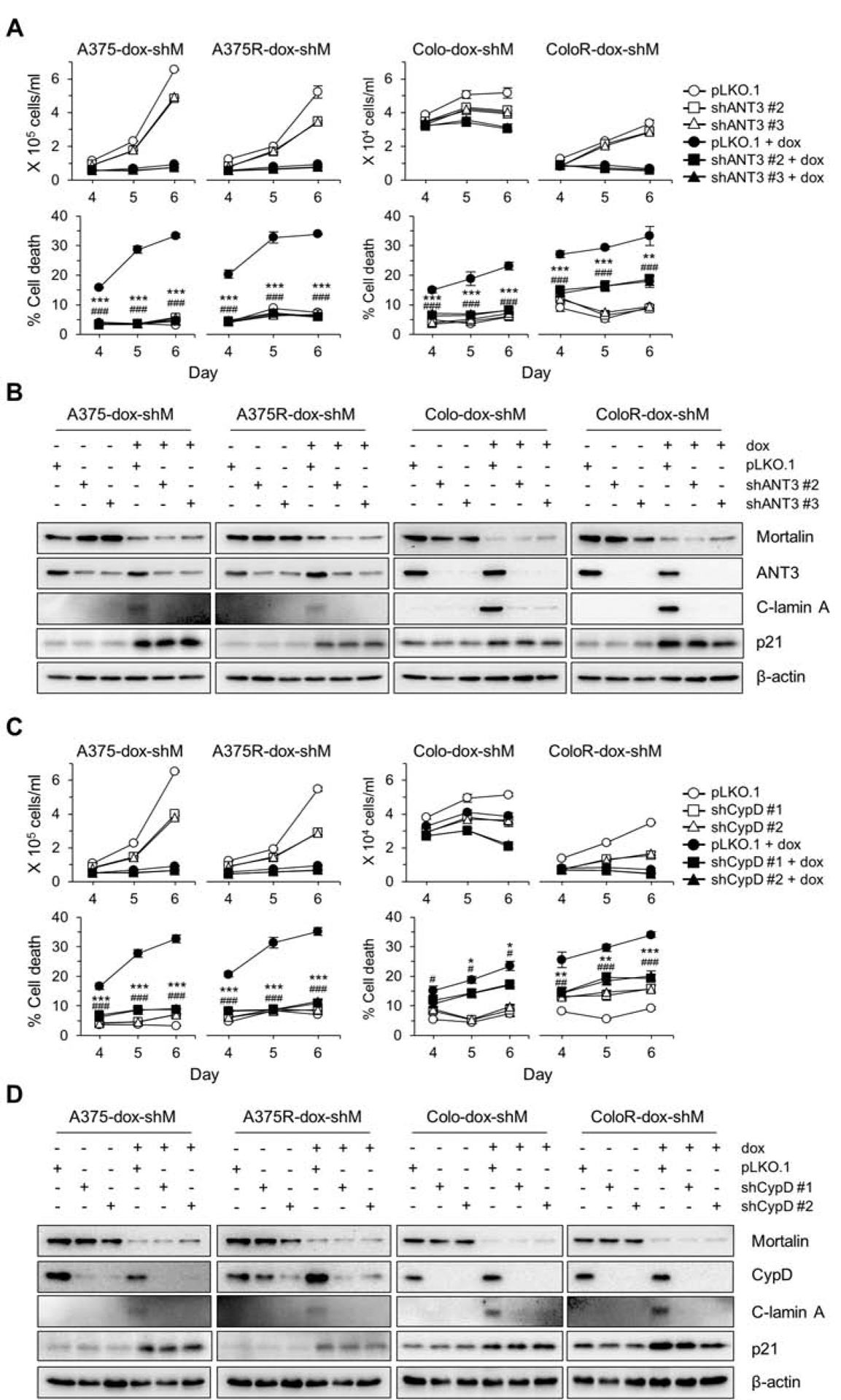
(A) Cell viability determined by TO-PRO 3 assay. Cells stably expressing pTRIPZ-dox-shMort (dox-shM) were infected with lentiviral pLKO.1-shANT3 or the control pLKO.1 for 24 hours prior to 5 day doxycycline (0.5 μg/mL) treatment. (B) Western blot analyses of total lysates of cells treated as described in (A). C-lamin A indicates cleaved lamin A. β-actin is the control for equal protein loading. Densitometry shown in supplemental figure S3A. (C) Cell viability determined by TO-PRO 3 assay. Cells stably expressing pTRIPZ-dox-shMort (dox-shM) were infected with pLKO.1-shCypD or the control pLKO.1 for 1 day prior to 5 day doxycycline (0.5 μg/mL) treatment. (D) Western blot analyses of total lysates of cells treated as described in (C). Densitometry shown in supplemental figure S3B. Blots are representative, and data (A and C) are mean ± SEM, n = 3. P values are relative to pLKO.1. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, and ### P < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. The asterisk and hash symbols for P values correspond to the first and the second RNA interference constructs, respectively.
