Figure 5. Effect of SC inactivation on attention-related modulation, change-evoked activity and detect probability in fSTS neurons was not specific to motion stimuli.
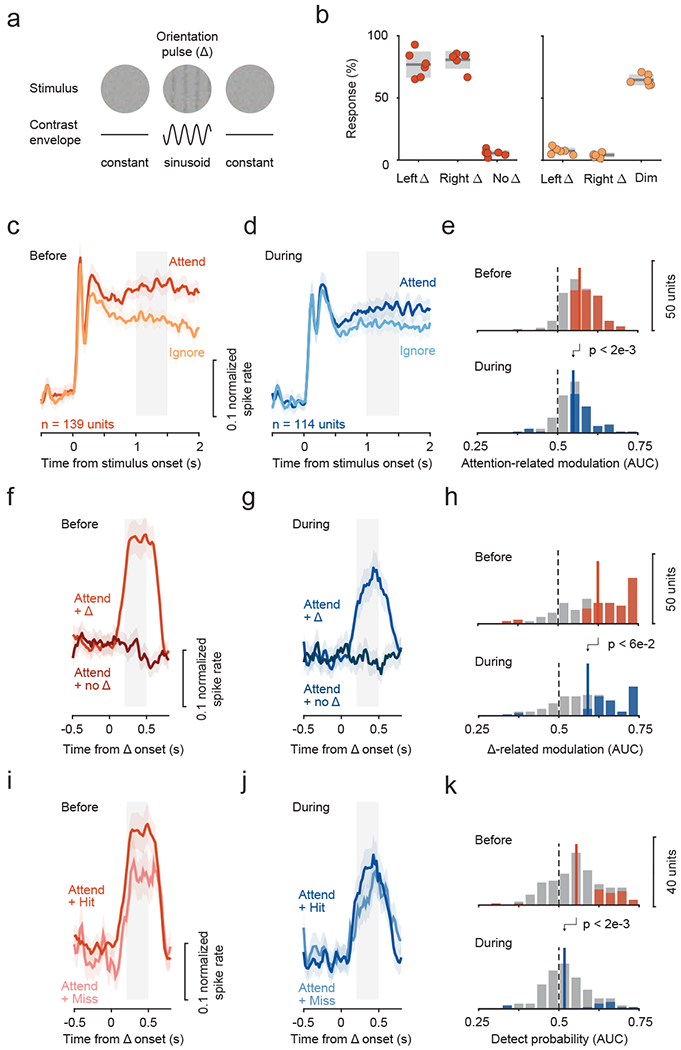
a. The monkeys’ task was to detect the brief appearance (0.5 s) of a 2nd order orientation pulse stimulus, that cannot be detected from its motion energy, from a dynamic white noise stimulus. The pulse was constructed by applying a sinusoidal contrast envelope on the white noise stimulus (see Methods).
b. Behavioral performance in the task for the attend (left panel) and ignore (right panel) conditions (similar format to figure 1a, b).
c-e. Attention-related modulation before and during SC inactivation (same format as figure 2a–c).
f-h. Change-related activity before and during SC inactivation (same format as figure 3a–c).
i-k. Detect probability before and during SC inactivation (same format as figure 4a–c).
See also figure S2.
