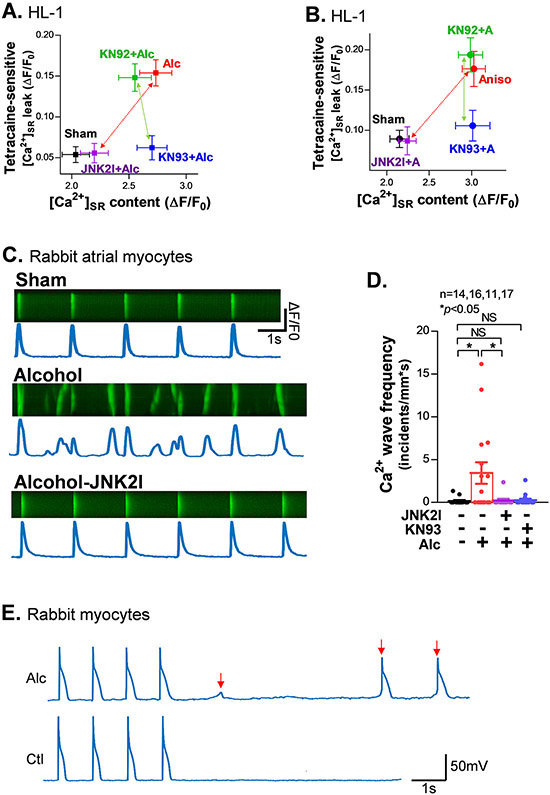
Figure 6.
JNK2 regulates a [Ca2+]SR load (CaMKII-independent) and leak (CaMKII-dependent) relationship, which driving arrhythmic activities in alcohol-exposed rabbit atrial myocytes. A-B) Plot of the amount of diastolic [Ca2+]SR leak and load in alcohol-exposed (A) and JNK activator anisomycin (Aniso or A)-treated (B) HL-1 myocytes in the presence of 1 μM KN93 or 1 μM KN92 compared to sham controls. Red arrows indicate completely attenuated higher SR Ca2+ leak and load by JNK2-specific inhibition (JNK2I) in both alcohol-exposed and anisomycin (Aniso or A)-treated (B) HL-1 myocytes and green arrows indicate abolished leak but unaffected load by CaMKII inhibition by KN93 but not KN92, an inactive analogue of KN93. C) Representative confocal images of normal Ca2+ transients (0.5Hz) from a sham-control myocyte (upper), multiple Ca2+ waves from an alcohol-exposed myocyte (middle), and normal Ca2+ transients from a JNK2I treated alcohol-exposed atrial myocyte (lower). D) Summarized data showing significantly increased frequency of pacing (0.5Hz)-induced Ca2+ waves in alcohol (Alc)-exposed atrial myocytes compared to sham controls, while these alcohol-evoked changes are eliminated by either JNK2 inhibitor (JNK2I) or CaMKII inhibitor KN93 treatment (far right bars). E) Representative action potential traces of alcohol-exposed (0.23%, 24 hr) and sham control rabbit myocytes showing delayed afterdepolarization (DAD) events at 1Hz electrical pacing, while no DAD events were induced in sham controls. DADs are indicated by the arrows in red.