Fig. 5. Effects of ultrasound on wound contraction and collagen deposition.
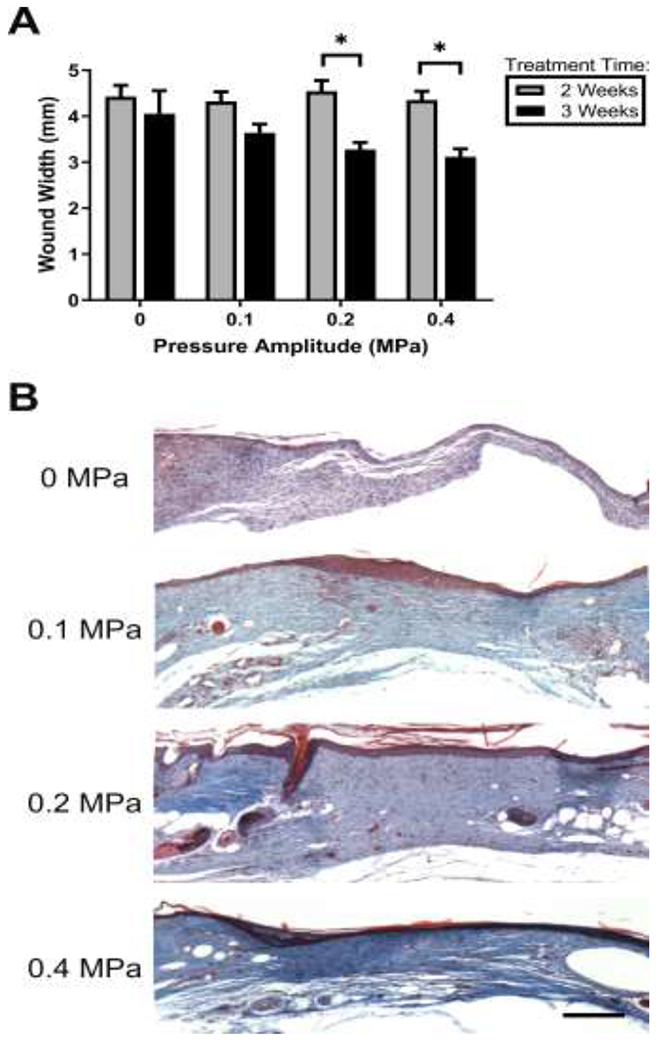
(A) Wound widths were determined by measuring the distance between the severed edges of the panniculus carnosus muscle layer using H&E-stained tissue sections from the center of each wound. **p < 0.01; 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. 2- and 3-week treatments were significantly different from one another at 0.2 and 0.4 MPa pressure amplitudes (p = 0.006 and p = 0.003, respectively). (B) Representative images of Masson’s trichrome-stained sections from the center of wounds exposed to pulsed ultrasound at 0, 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 MPa for 3 weeks. Scale bar = 200 μm.
