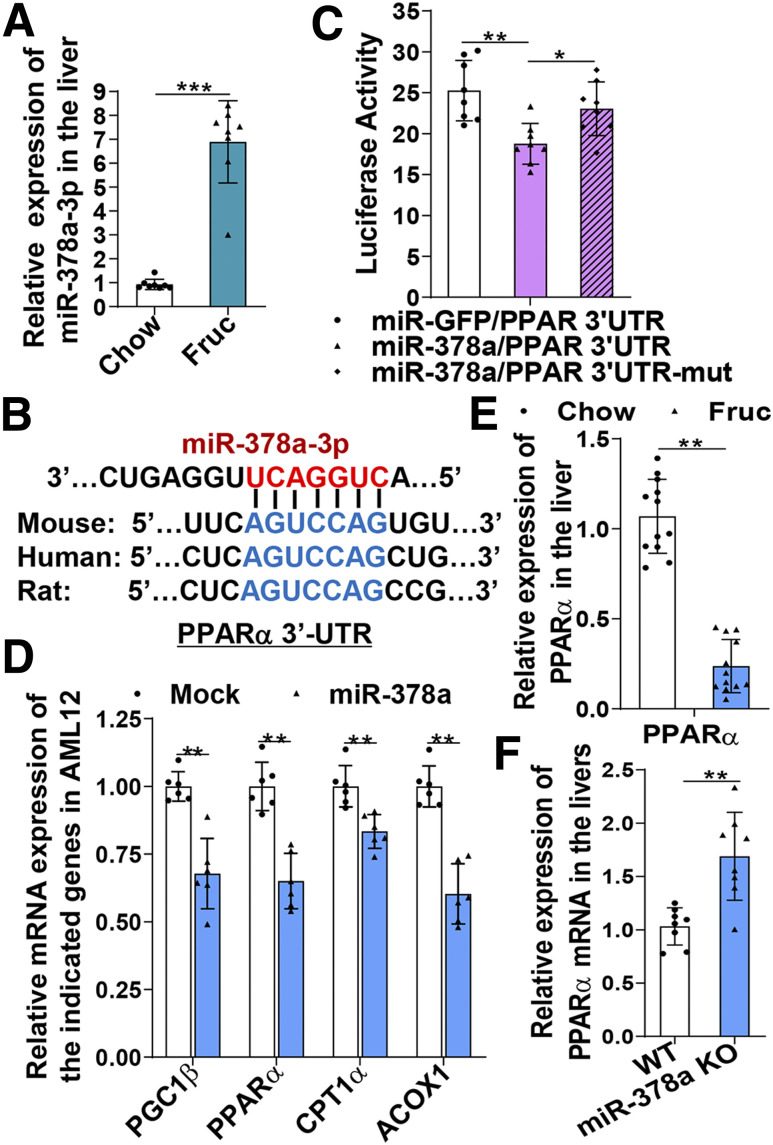
Figure 1.
Upregulation of miR-378a induced by a high-fructose diet targets the PPARα signaling pathway. Mice (C57BL/6J) were subjected to chow or fructose diets for 4 weeks. Total miRNAs were extracted from the livers. A: Hepatic miRNA-378a-3p detected by a TaqMan miRNA probe specific for miR-378a and normalized to small nucleolar RNA202 (n = 8/group). B: miR-378a-3p response elements within the 3′-UTR of human, rat, and mouse PPARα mRNAs predicted by TargetScan. C: COS-7 cells were cotransfected with miR-GFP or miR-378a plus the firefly luciferase reporter of WT PPARα 3′-UTR or mutant PPARα 3′-UTR for 48 h. Cell lysates were examined for firefly luciferase activities and normalized to Renilla luciferase activities. D: AML12 cells were transfected with miR-378a or a mock vector (GFP) for 48 h. mRNAs of the indicated genes were detected by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). E: mRNA of PPARα detected by qRT-PCR in the livers of 4-week chow-fed or fructose-fed mice (C57BL/6J, n = 12/group). F: mRNA of PPARα detected by qRT-PCR in the livers of WT and miR-378a-KO mice (n = 8/group). Data are mean ± SD. The two-tailed Student t test was used for statistical analyses of two-group comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. controls. Fruc, fructose; mut, mutant.