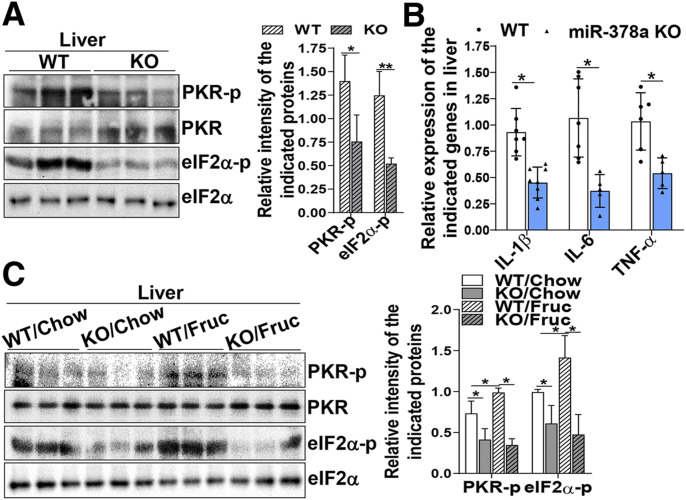
Figure 5.
Depletion of miR-378a by genetic intervention or anti-miR-378a oligonucleotides improves fructose-induced insulin resistance. A and B: miR-378a-KO mice and their WT littermates were fasted for 12 h. Liver tissues were collected for the following analyses: immunoblotting analysis of PKR phosphorylation (active form) and its substrate eIF2α using phosphorylation-specific antibodies against PKR and eIF2α (n = 6/group) (A) and mRNA expression of the indicated inflammatory cytokine genes determined by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 5–7/group) (B). C: Immunoblotting analysis of PKR phosphorylation and its substrate eIF2α in the liver tissues of WT and miR-378a-KO mice fed a chow or high-fructose diet for 4 weeks (n = 5/group). Data are mean ± SD. The two-tailed Student t test was used for statistical analyses of two-group comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. controls. Fruc, fructose; PKR-p, phosphorylated protein kinase R.