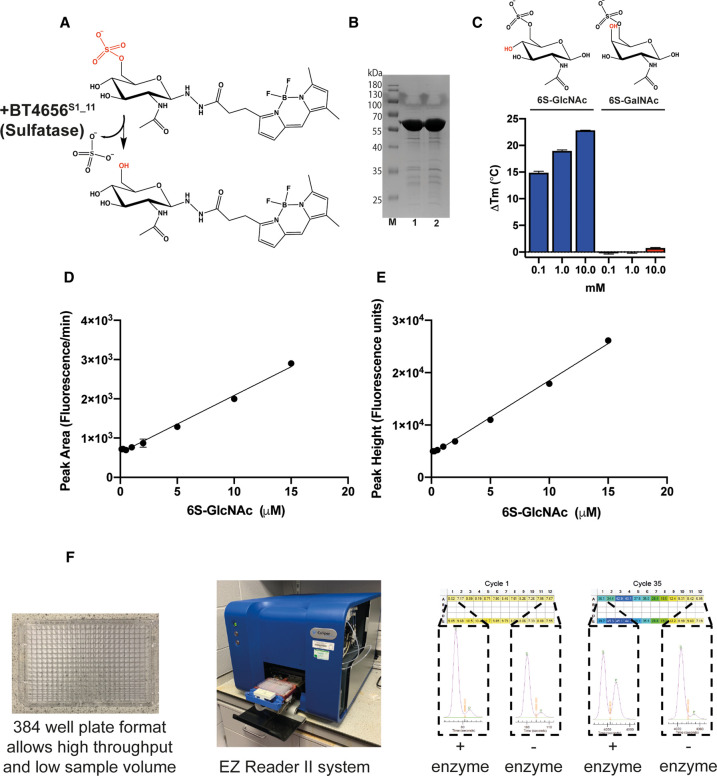
Figure 1. Substrate and enzyme analysis, and concentration-dependent linear detection of BODIPY-labelled 6S-GlcNAc substrate using a high-throughput microfluidic assay.
(A) Structure of the BODIPY-FL hydrazide labelled substrate 6S-GlcNAc substrate, the β anomer is depicted, but glycosylamines are also able to undergo mutarotation, and the structure of the product after action by BT4656S1_11. (B) M is the protein ladder and lanes 1 and 2 contain catalytically active Hexa His-tagged BT4656S1_11 (Ser77Cys) and the catalytically-inactive (wild-type) Hexa His-tagged BT4656S1_11 (Ser77) carbohydrate sulfatase, respectively, both migrating at ∼62 kDa. Both were purified to near homogeneity using cobalt-based immobilised affinity chromatography. After dialysis, 8.5 μg of purified protein was separated by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. (C) Differential scanning fluorimetry was used to calculate midpoint denaturation temperature (Tm) values for the catalytically inactive wild-type form of BT4656S1_11 in the presence of its cognate substrate, 6S-N-acetyl-glucosamine, and the non-binding C4 epimer 6S-N-acetyl-galactosamine; (D) LED-induced fluorescence of fluorescent substrate using EZ Reader II system. Peak area and (E) peak height was plotted as a function of substrate concentration. Assays were conducted as described in the Methods; (F) depicts the experimental setup and the data output produced by the EZ reader II system. As the ratio of substrate to product changes, i.e. an increase in product and decrease in substrate, a conversion heatmap is produced allowing easy visualisation of the enzymatic reaction as it proceeds.