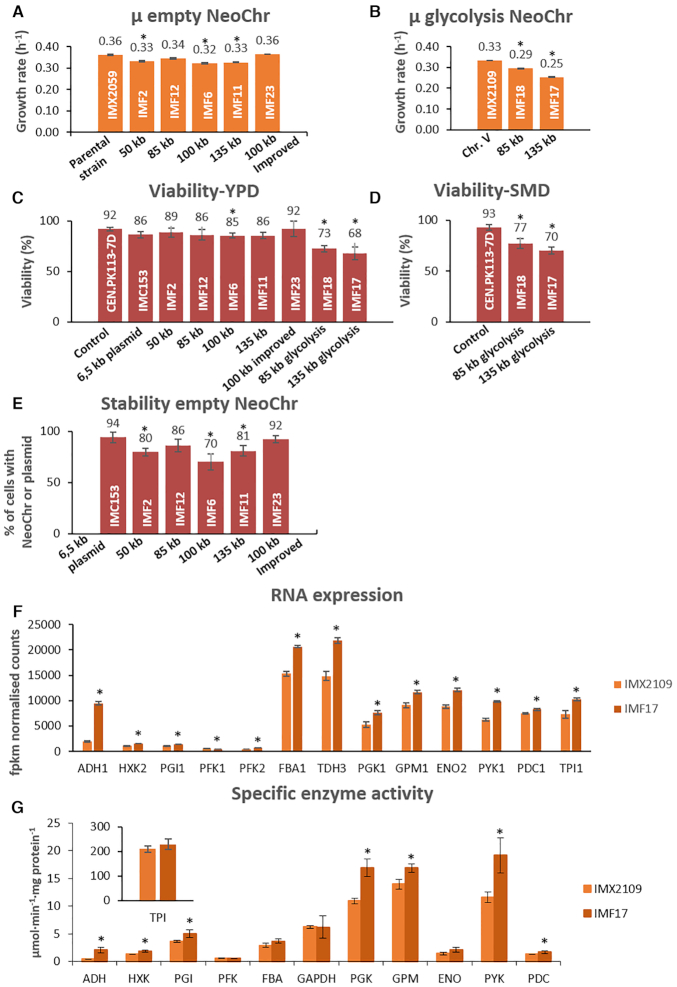
Figure 5.
Physiological characterization of strains carrying synthetic chromosomes. (A and B) Specific growth rate of strains carrying empty neochromosomes (Panel A: IMF2, IMF12, IMF6, IMF11 and IMF23) and glycolytic neochromosomes (Panel B: IMF18 and IMF17). Growth rates represent the average and mean deviation of biological duplicates except for the parental strain which cultures were performed in biological quadruplicate. (C and D) Viability measured as number of colonies on YPD (C) or SMD (D) sorted by FACS, divided by the total number of possible colonies (96), for the empty and glycolytic neochromosomes. Data represent biological duplicates and are averaged from 4 days of measurement for all strains except for the 100 kb improved design (two samples at day 1 and day 4). (E) Stability measured as the number of transformants on selective plates (SMD) divided by the number of colonies on non-selective plates (YPD). For each strain, the stability represents the average of 4 days of measurement in biological duplicates, except for 100 kb improved design (IMF23) for which 2 days of measurement were used (day 1 and day 4). (F) Transcript levels of the glycolytic genes from IMF17 (135 kb glycolysis neochromosome) and control strain IMX2109 expressing glycolysis from native chromosome V, grown in aerobic batch cultures. Transcript levels and standard deviations are from biological triplicates. (G) Specific activity of glycolytic enzymes in IMF17 and control strain IMX2109 from aerobic batch cultures. Activities were measured at least in biological duplicates. For panels A, B, C, D and E all significant differences with respect to the first bar are indicated with an asterisk (one-way ANOVA with Post-Hoc Tukey–Kramer, P< 0.05). For panels F and G, the asterisk indicates whether transcript levels or enzyme activities of IMF17 are significantly different with respect to IMX2109 (two-tailed paired homoscedastic t-test P< 0.05).