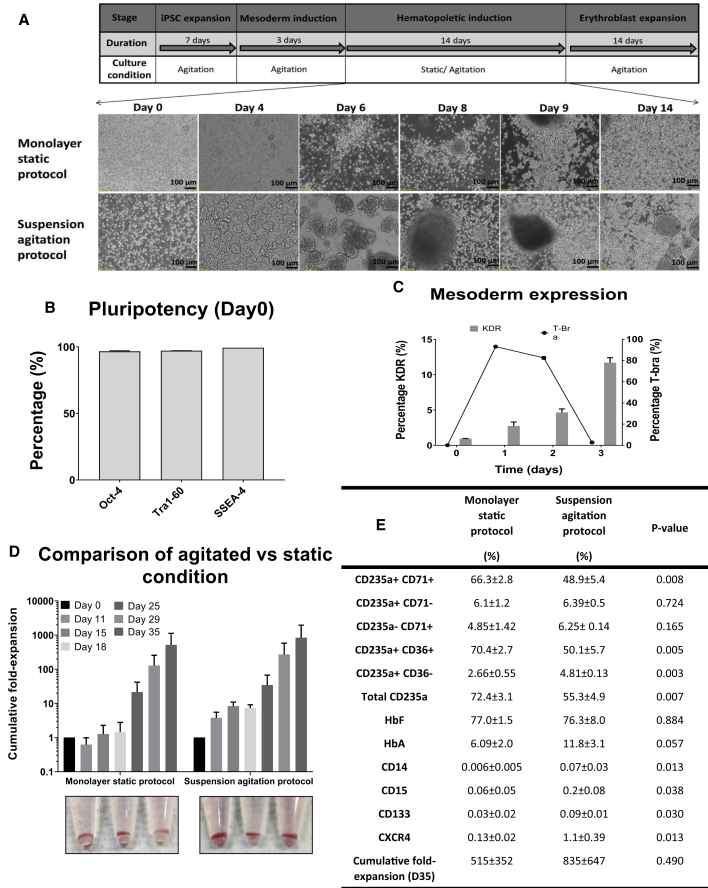
Figure 1.
Development of Agitation Suspension Culture Differentiation of O-Neg hiPSCs
(A–C) (A) Schematic of differentiation process from hiPSC to erythroblast stage. Bright-field images of cells from an O-neg hiPSC line, D5, undergoing hematopoietic differentiation in tissue culture plates under static conditions (monolayer static protocol) or in 6 well ULA plates under continuous agitation (suspension agitation protocol) from day 0 to 14 of the hematopoietic induction stage. Flow cytometry evaluation of (B) pluripotency markers following 7 days of agitation expansion in 6 well ULA plates and (C) T-Bra and KDR cell populations during mesoderm differentiation.
(D) Cumulative fold expansion of total viable cells following differentiation using monolayer static protocol or suspension agitation protocol and corresponding hemoglobinized cell pellets observed at day 35 of differentiation. There is no significant difference in expansion fold between static and agitated conditions, p > 0.05.
(E) Table summarizing FACS characterization of differentiated cells from day 35 of differentiation. Percentages of erythroid-specific markers CD235a, CD71, and CD36 and fetal/adult hemoglobin expression as well as markers for myelomonocytic cells (CD14, CD15) and hematopoietic stem cells (CD133, CXCR4) are shown together with cumulative fold expansion on day 35. All data represent the mean ± SD with at least three independent replicates. Representative experiment shown.