Figure 1.
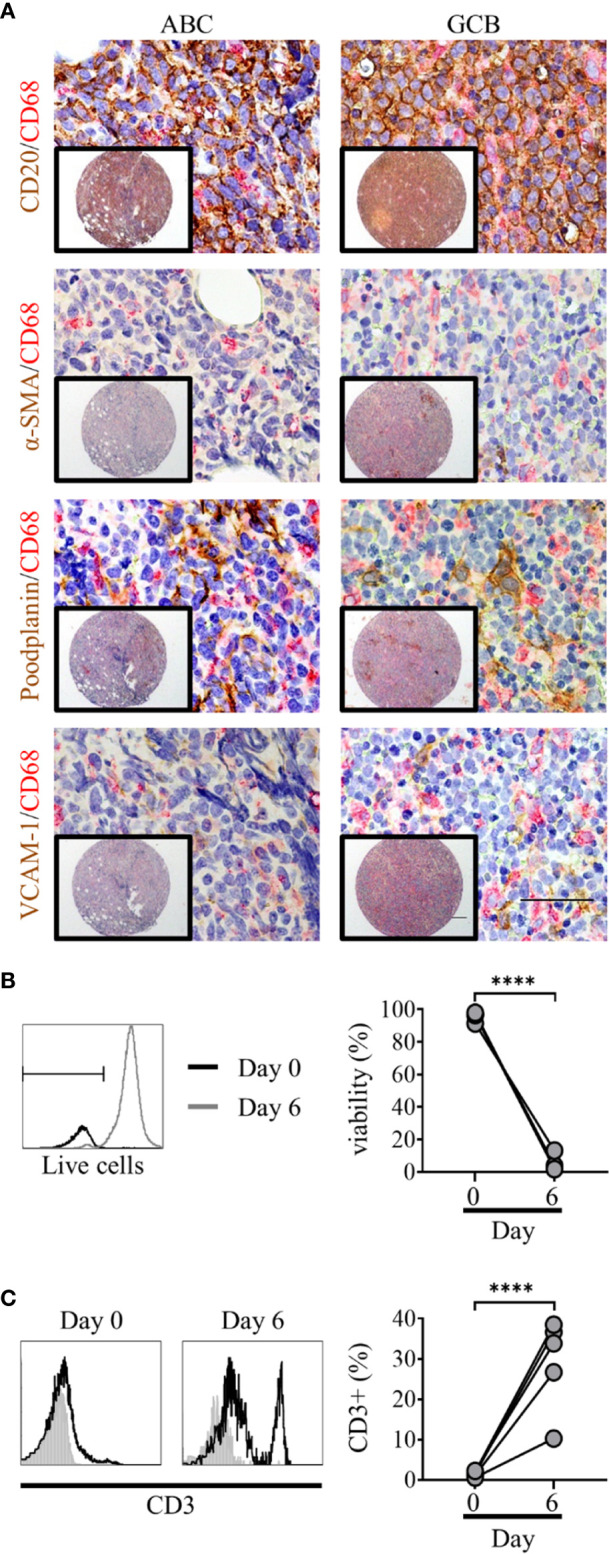
Primary diffuse large cell B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells exist within a complex multicellular environment and die in vitro. (A) Double immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of DLBCL cells (CD20, brown) or lymphoid fibroblasts [alpha smooth muscle Actin (α-SMA), podoplanin, and VCAM-1 (brown)] and macrophages (CD68, red) of activated B cell-like (ABC) (left hand panels) and germinal-center B cell-like (GCB) (right-hand panels) DLBCL tumor micro-array samples, demonstrating the close interaction of all three cell types within the tumor microenvironment. Scale bars: 200 µm, inset image, 50 µm main image. (B) Representative histograms of live/dead viability staining of primary DLBCL cells pre (day 0, black line) and post 6 days of in vitro culture (grey line); marker denotes the cut-off for live staining (dead cells stain more intensely). Graph shows pre- and post-culture viability, each filled circle represents an independent experiment. Statistical significance between groups was assessed using a paired two tailed t-tests, ****p < 0.0001. (C) Representative histograms showing CD3 staining in primary DLBCL cell suspensions before (day 0) and after 6 days of in vitro culture. Graph shows pre- and post-culture percentages of CD3+ lymphocytes, each filled circle represents an independent experiment. Statistical significance between groups was assessed using a paired two tailed t-tests, ****p < 0.0001.
