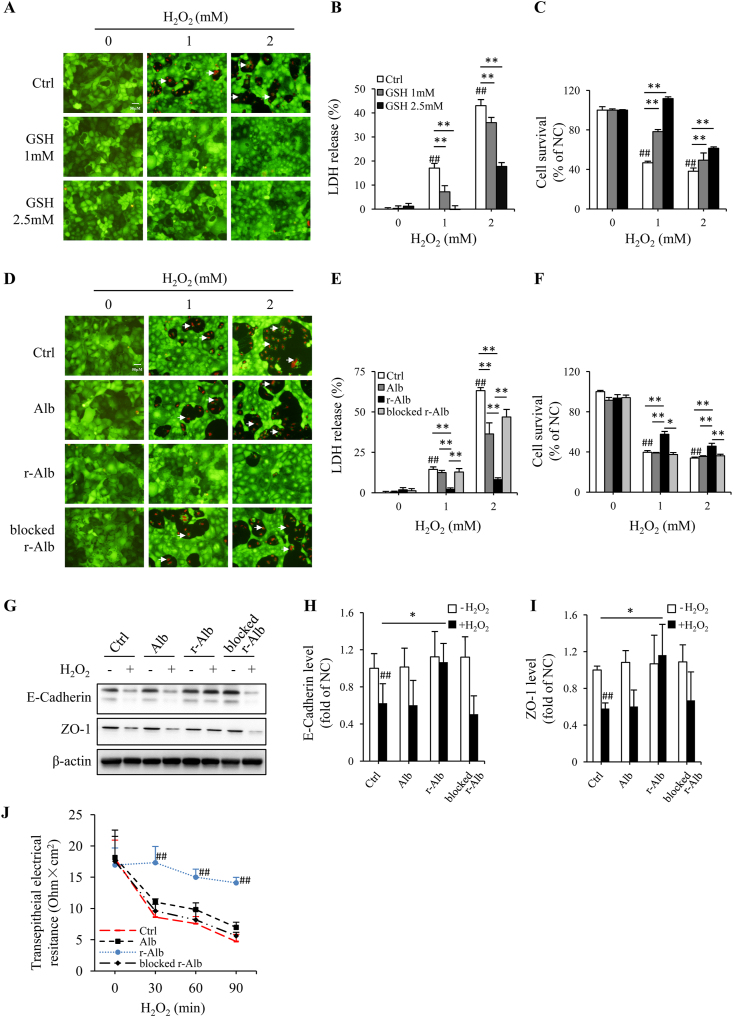
Fig. 6.
Thiol antioxidant GSH and r-Alb prevent H2O2-induced oxidative cell injury in colon epithelial cell line Caco-2. (A–F) Induction of oxidative cell injury by H2O2 and its prevention by thiol antioxidant GSH and r-Alb. Cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of H2O2 in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of GSH or 5 mg/ml modified Alb for 6 h. The cell viability was determined using Calcein AM/PI staining (A, D), LDH release (B, E), and formazan formation (C, F). The PI-positive dead cells in (A, D) have been arrow-marked. The data in B, C, E and F are mean ± SD (n = 4; ##P < 0.01 vs. NC; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (G–I) Effect of differently modified Alb on H2O2-induced changes in E-Cadherin and ZO-1. Cells were exposed to 600 μM H2O2 in the presence or absence of 2.5 mg/ml modified Alb for 3 h. The cellular proteins were extracted and subjected to Western blot analysis for E-cadherin and ZO-1 (G). The densitometric analysis of the blot in G is shown in H and I. The results are expressed as the percentage of change relative to untreated control. Data shown are mean ± SD from four separate experiments (n = 4; ##P < 0.01 vs. NC; *P < 0.05). (J) Time-course effect of differently modified Alb on H2O2-induced disruption of barrier function. Confluent Caco-2 cells were exposed to 2 mM H2O2 in the presence or absence of differently modified Alb (5 mg/ml) for the indicated time intervals and subjected to TER measurement. TER was expressed as the ratio of voltage to current normalized by the area of the monolayer. Data shown are mean ± SD (n = 4; ##P < 0.01 vs. respective control).