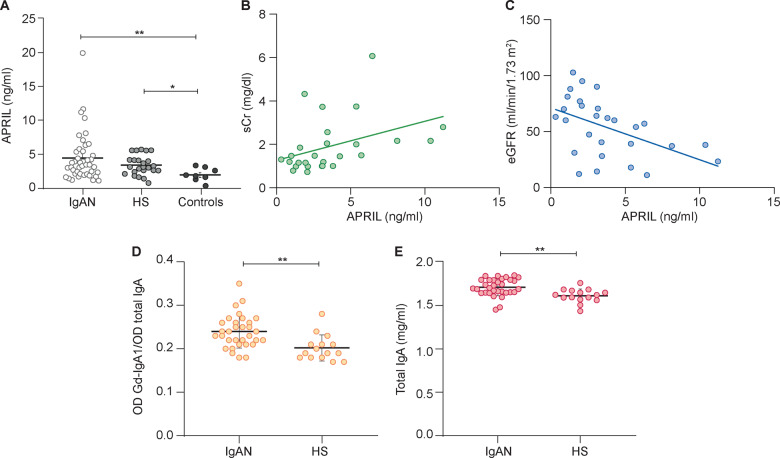
FIGURE 2.
Serum APRIL levels were significantly higher in IgAN patients and correlated with creatinine serum level. (A) Serum levels of APRIL were determined by ELISA in 44 IgAN patients, 23 HSs and 8 controls and were significantly higher in IgAN patients and HSs than non-IgA glomerulonephritis patients (controls). APRIL IgAN patient serum levels correlated with (B) serum creatinine (P = 0.04) and (C) eGFR determined by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation (P = 0.008) (Spearman’s correlation). (D) Serum levels of Gd-IgA were evaluated in IgAN patients and HSs. The relative lectin binding per unit of IgA1 was calculated as the optical density (OD) value of lectin over the OD value of total IgA. The results showed that serum levels of Gd-IgA1 were higher in IgAN patients than HSs. (E) Serum total IgA levels in IgAN patients and HSs were determined by ELISA and were significantly higher in IgAN patients (P = 0.001). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.005.