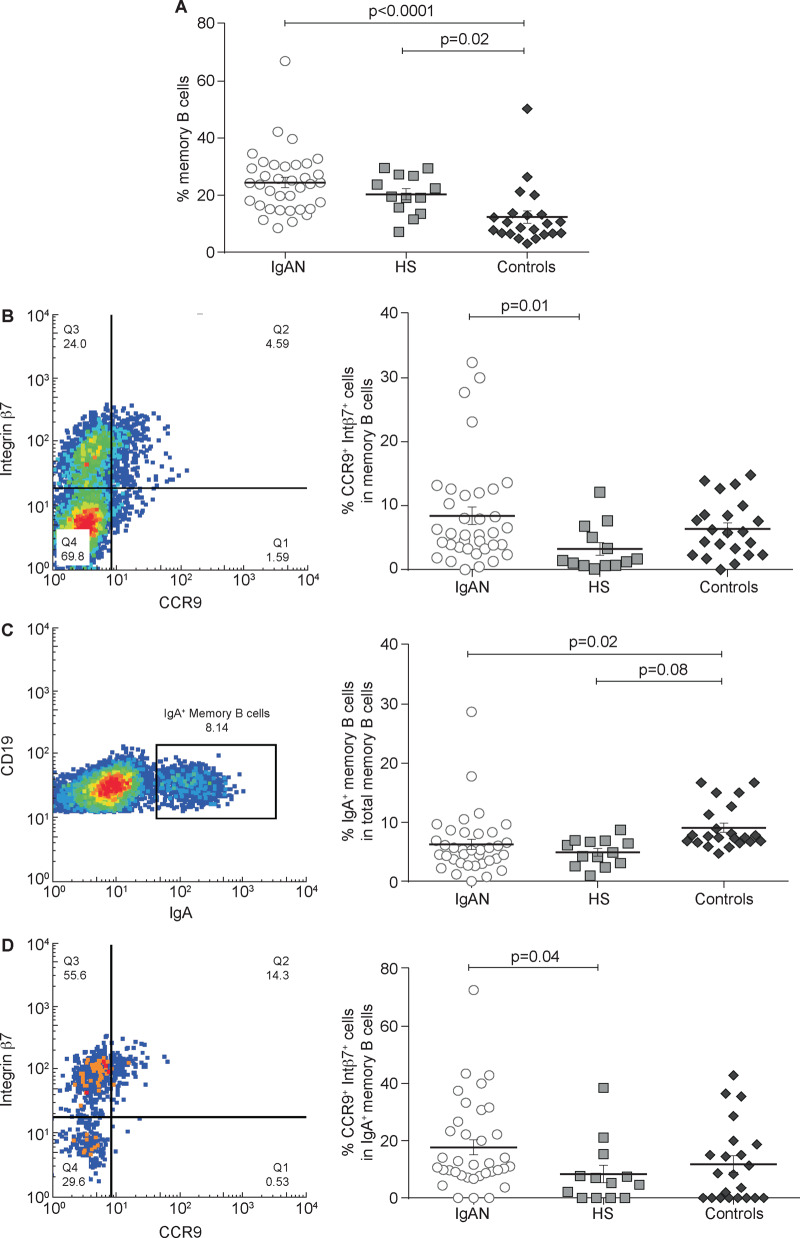
FIGURE 5.
Total memory B-cell subsets analysis in IgAN patients compared with HSs and controls. PBMCs were isolated from the peripheral blood of 36 IgAN patients, 13 HSs and 22 patients with non-IgA glomerulonephritis (controls) and analysed by flow cytometry. (A) The total memory B-cell subpopulation was analysed in IgAN patients, HSs and controls. The total memory B cells percentage was highest in IgAN patients compared with controls (P < 0.0001) and HSs. Controls had a lower percentage of memory B cells compared with both IgAN patients and HSs (P = 0.02). (B) Mucosa-activated (CCR9+ integrin β7+) memory B cell frequencies in IgAN patients, HSs and controls. Percentages of mucosa-activated memory B cells were increased in both IgAN (P = 0.01) and controls compared with HSs, indicating an involvement of mucosal immune response in glomerulonephritis. (C) IgA+ memory B cell frequencies in IgAN patients, HSs and controls. No difference was found between IgAN patients and HSs, whereas controls had a higher percentage of IgA+ memory B cells compared with IgAN patients (P = 0.08) and HSs (P = 0.02). (D) Mucosa-activated (CCR9+ integrin β7+) IgA+ memory B cells frequencies in IgAN patients, HSs and controls. The intestinal-derived IgA+ memory B cells were significantly increased in IgAN patients but not in patients with non-IgA glomerulonephritis compared with HSs (P = 0.04). One-way ANOVA was used to compare groups.