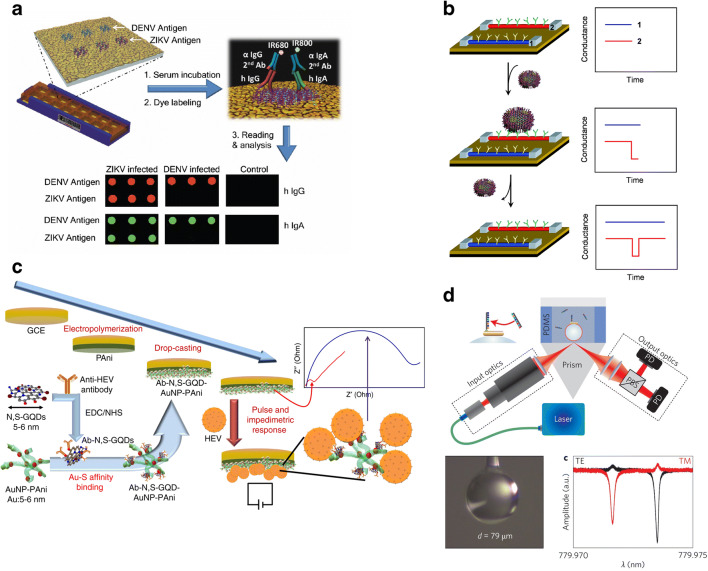
Fig. 7.
Virus detecting methodologies, utilizing materials: (a) Multiplexed microarrays with plasmonic gold (pGold) nanostructures and near-infrared fluorescence molecules having Zika and dengue antigens (triplicate). Human serum containing antibodies against Zika (ZIKV) and dengue (DENV) viruses are discharged in the microarrays. Thereby, antibodies get captured by the antigens on the microarrays. Antibodies are tagged with a mixture of fluorescent dyes [anti-human immunoglobulin G-infrared fluorescent dye 680 (IgG-IRDye680) and immunoglobulin A-infrared fluorescent dye 800 (IgA-IRDye800)]. The microarray (biochip) is thereby scanned in a fluorescence reader indicating the binding of antibodies and antigens [94] (Reproduced with permission from publisher). (b) Antibodies, embedded in nanowires binds with the viruses and thereby, change in the conductance of the nanowires is observed [95] (Copyright (2004) National Academy of Sciences, U.S.A.). (c) Pulse-induced impedimetric biosensors using electrode matrix of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and polyanaline nanowires embedded with gold (AuNP-PAni) to detect the hepatitis E virus (HEV). The HEV is captured through nitrogen-linked anti-HEV antibody (Ab) attached to sulfur co-doped GQDs and AuNp-PAni (Ab-N, S-GQDs@AuNP-PAni) while a pulsed external E-field is applied to observe the impedimetric response [96] (Open Access). (d) Plasmonic gold nanorod-based biosensors to sense the single RNA molecule [97] (Reproduced with permission from publisher). Abbreviations: EDC, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride; GCE, glass carbon electrode; NHS, N-hydroxysuccinimide; N, S-GQDs, nitrogen and sulfur codoped grapheme quantum dots; PBS, polarizing beam splitter; PD, photo-detector; PDMS, polydimethylsiloxane