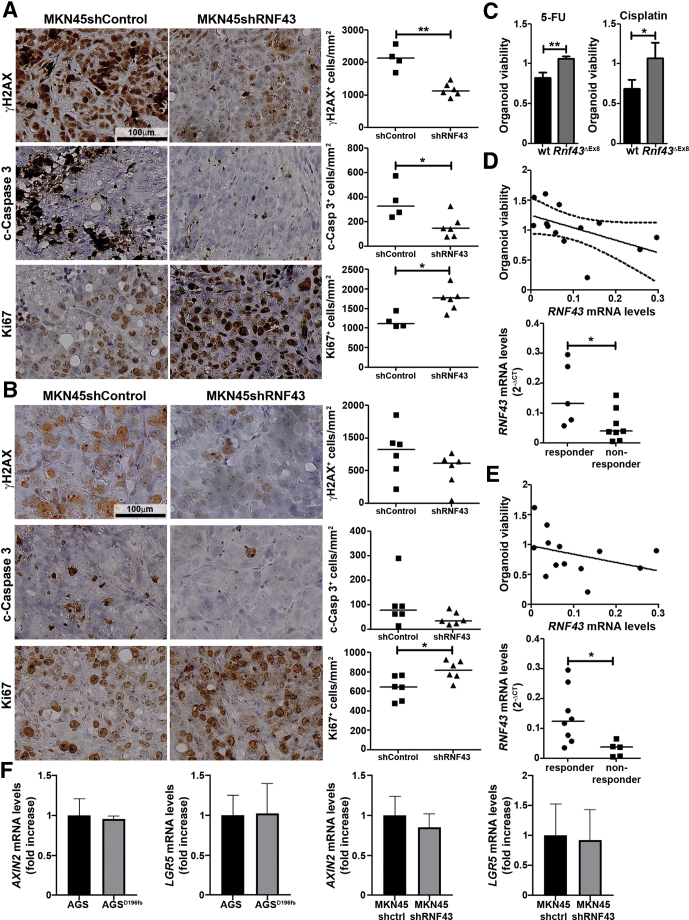
Figure 4.
RNF43 influences susceptibility to DNA damage-inducing chemotherapeutics. Representative images showing γH2AX, cleaved caspase 3 (c-caspase 3), and Ki67 detected by immunohistochemistry in xenograft tumors that originated from control MKN45 (shCtrl) and RNF43 knockdown MKN45 (shRNF43) cells after treatment with (A) 5-fluorouracil or (B) cisplatin. Quantification of positive cells per square millimeter is shown. Each dot represents 1 mouse. (C) Viability of gastric organoids from WT or Rnf43ΔEx8 mice after treatment with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or cisplatin. Values were normalized over untreated (N = 3). Spearman correlation between RNF43 mRNA expression levels in human gastric tissue samples (N = 13), and viability of organoids generated from the same tissue samples after treatment with (D) 5-fluorouracil or (E) cisplatin. RNF43 mRNA levels normalized to GAPDH also are shown. (F) AXIN2 and LGR5 mRNA levels in AGS, AGSD196fs, and MKN45 control and RNF43 knockdown cells. Cycle threshold (CT)values were normalized to GAPDH and fold change was calculated over control cells (N = 3). Error bars indicate SD. Horizontal lines represent the median values. ∗P ≤ .05, ∗∗P ≤ .01, (C and F) 2-tailed unpaired t test, (A, B, D, and E) Mann–Whitney test. mRNA, messenger RNA.