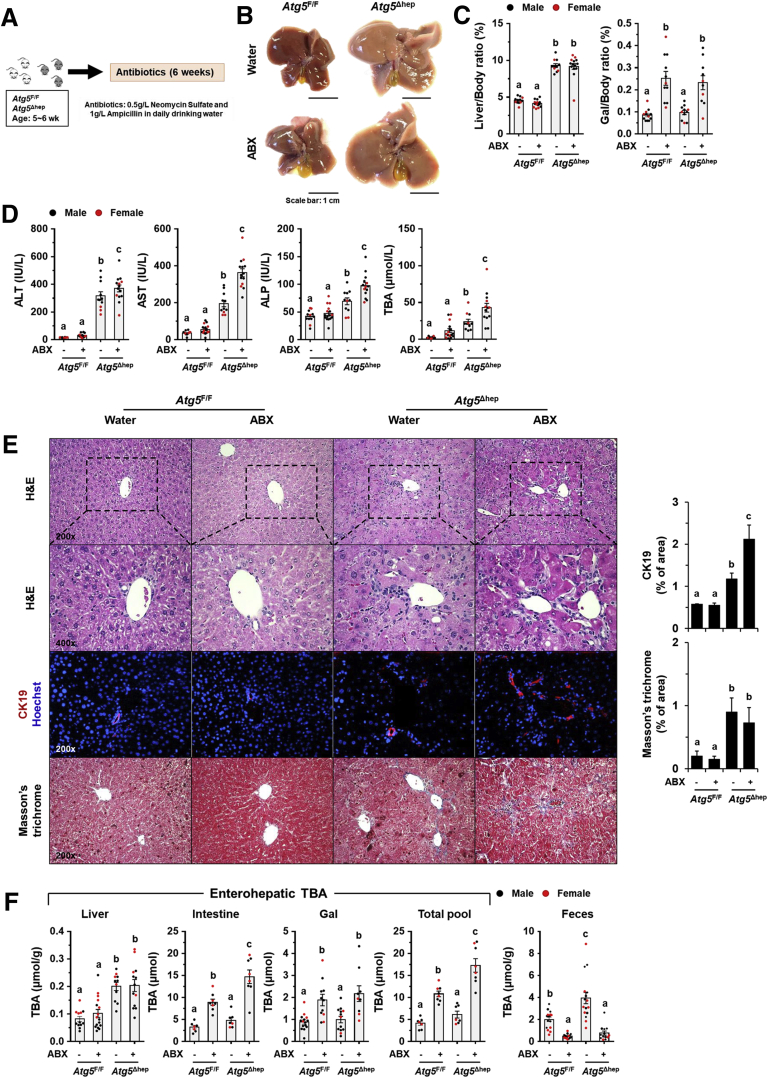
Figure 3.
ABX treatment aggravated Atg5 deficiency-induced liver injury. (A) Scheme of the ABX treatment. Mice were given neomycin sulfate and ampicillin sodium salt mixture in daily drinking water for 6 weeks. (B) Representative gross anatomy of livers of indicated genotypes and treatments. (C) Liver weight and gallbladder (Gal) weight were determined as percentages of the body weight (n = 10–16/group). (D) Serum levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and TBA in mice (n = 10–16/group). (E) Liver sections were subjected to H&E, anti-CK19, or Masson’s trichrome staining. Percentage of positive area was quantified with ImageJ (anti-CK19 staining quantification, n = 3–4/group; Masson’s trichrome staining quantification, n = 8–12/group). (F) TBA levels in indicated compartments were measured (n = 7–16/group). Data are shown as means ± SE. Groups with different lowercase letters had significant differences (P < .05).