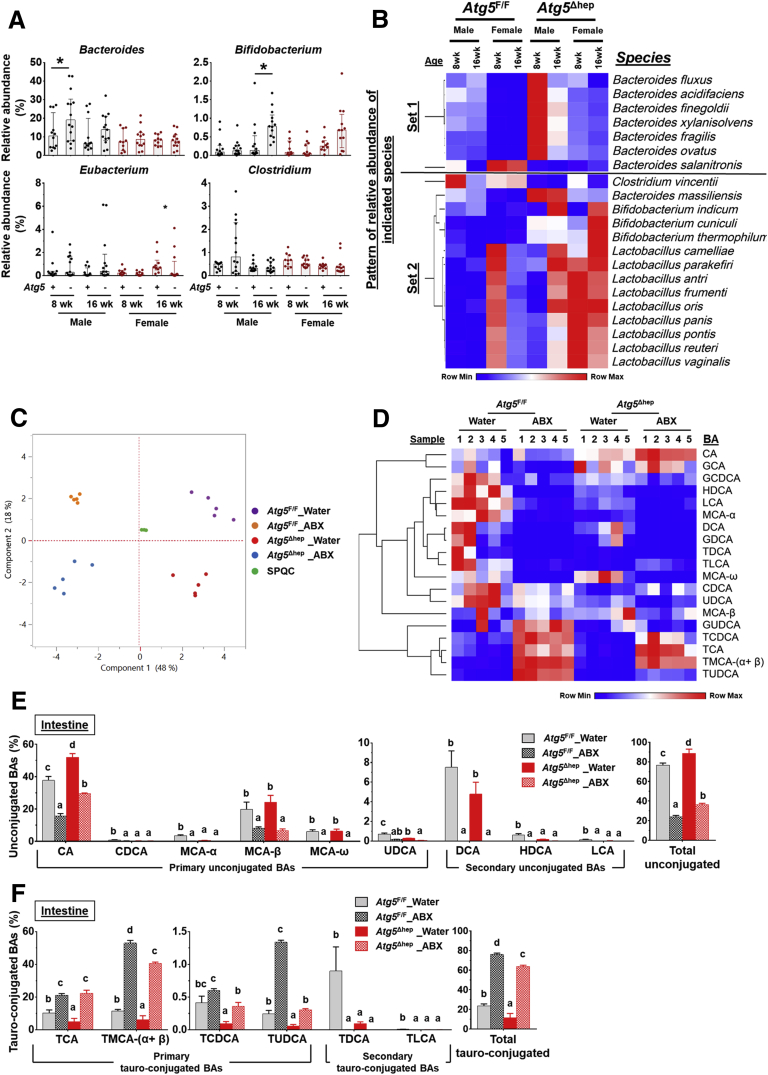
Figure 6.
Hepatic autophagy deficiency affects intestinal BA composition in correlation with gut dysbiosis. (A) Hepatic autophagy deficiency affected the proportion of bacteria with the BSH and/or 7α/β-dehydroxylation activities at the genus level (Lactobacillus is shown in Figure 1E). Data are shown as median with interquartile range, n = 10/group. (B) Heatmap shows the BA-metabolizing bacteria that are disproportionate in Atg5Δhep mice at the species level. Heatmap was generated, and values in the heatmap were mapped to colors using the minimum and maximum of each row independently. The hierarchical cluster of different species was constructed using one minus Pearson correlation method. Proportion of bacteria in Set 1 was significantly changed in both male and female Atg5Δhep mice at 8 weeks old. Proportion of bacteria in Set 2 was significantly changed in both male and female Atg5Δhep mice at 16 weeks old. (C) PCoA of BAs in the intestine data (log2-scaled μmol/L). (D) Heatmap was generated, and values in the heatmap were mapped to colors using the minimum and maximum of each row independently. Heatmap shows the cluster of indicated BA species in the intestine of different groups of mice. The hierarchical cluster of different BAs was constructed using one minus Pearson correlation method. (E and F) Intestinal levels of unconjugated (E) and tauro-conjugated (F) BAs in male mice. Data are shown as percentage of TBA level (means ± SE), n = 5/group. Groups with different lowercase letters or indicated by asterisk had significant differences (P < .05). HDCA, hyodeoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid.