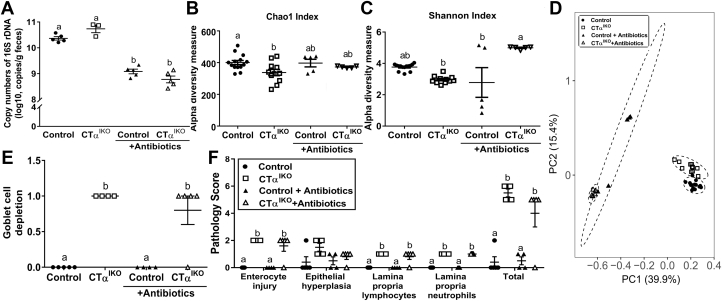
Figure 7.
Loss of intestinal CTα changes the microbiome but depletion of gut microbes with antibiotics does not prevent colitis development in CTαIKO mice. (A) Copy number of 16S rRNA in feces of control mice and CTαIKO mice treated with and without antibiotics (n = 3–5/group). (B) Chao1 and (C) Shannon indexes of gut microbiota from control mice and CTαIKO mice treated with and without antibiotics (control, n = 14; CTαIKO, n = 11; control + antibiotics, n = 5; CTαIKO + antibiotics, n = 5). (D) Principle component analysis plots of the bacterial communities based on the Bray–Curtis distance matrix. Each point represents an individual mouse (control, n = 14; CTαIKO, n = 11; control + antibiotics, n = 5; CTαIKO + antibiotics, n = 5). (E) Pathology score for goblet cell depletion in the colons of control mice and CTαIKO mice treated with and without antibiotics (n = 4–5/group). (F) Pathology scores of control mice and CTαIKO mice treated with and without antibiotics (n = 4–5/group). Columns that do not share a letter (a, b, or c) are significantly different (α = .05).