FIGURE 5.
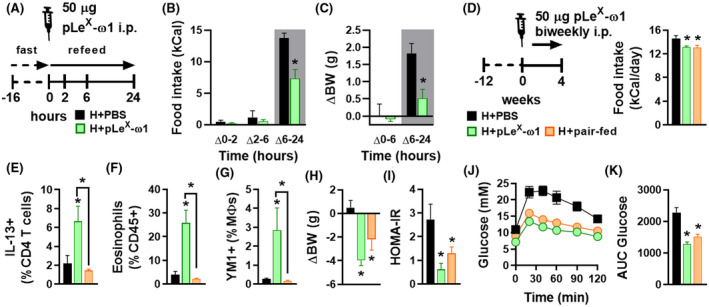
pLeX‐ω1 inhibits fasting‐induced refeeding and improves metabolic homeostasis through inhibition of food intake in obese mice. Mice were fed a HFD for 12 weeks and fasted overnight prior to intraperitoneal injections of either PBS (black bars) or 50 µg pLeX‐ω1 (green bars; A). Food intake (B) and body weight changes (C) were next monitored during 24 hours after refeeding. Mice were fed a HFD for 12 weeks, single‐housed, and next received biweekly intraperitoneal injections of PBS or 50 µg pLeX‐ω1 during 4 weeks. In one group (H + pair‐fed; orange bars), the amount of food available for PBS‐treated mice was adjusted daily in order to match the food intake of the pLeX‐ω1‐treated group (D). At the end of the experiment, eWAT was collected, processed, and analyzed as described in the legend of Figure 1. The frequencies of IL‐13‐expressing CD4 T cells (E), eosinophils (F), and YM1+ macrophages (G) were determined. Body weight change (H) was determined after 4 weeks. HOMA‐IR (I) was calculated at week 4 and an i.p. glucose tolerance test (J and K) was performed at week 3, as described in the legend of Figure 1. Results are expressed as means ± SEM. *P < .05 vs HFD or as indicated (n = 3‐5 mice per group)
