Figure 2.
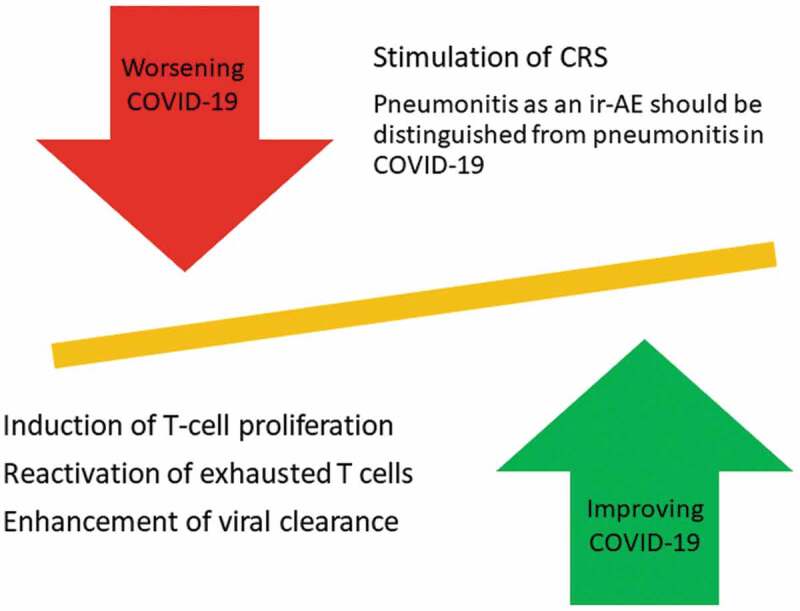
Risks and benefits of ICI administration in patients with COVID-19
By interfering with the transduction of inhibitory signals through PD-1/PD-L1 or CTLA-4 or other inhibitory receptors, ICI can improve the number and function of T cells in patients with COVID-19 and subsequently enhance the rate of viral clearance by T cells. However, there is still a probability of inflammatory cytokine release exacerbation by reactivation of the exhausted T cells in the immune system. Moreover, potential interference/overlap between pneumonitis caused by COVID-19 infection and as an adverse event of ICI should be considered and studied. Moreover, detailed guidelines to distinguish these two etiologically different respiratory complications should be provided.
CRS: cytokine storm syndrome, ir-AE: immune-related adverse event
