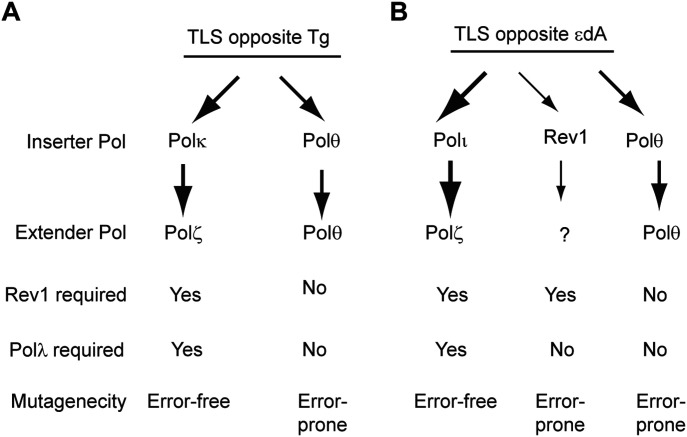
Figure 7. TLS pathways for replication through Tg and εdA lesions.
(A) TLS pathways for replication through Tg. After nt insertion by Polκ, Polζ extends synthesis. Polλ’s scaffolding role is required for Polζ function in TLS. This pathway conducts error-free TLS through the Tg lesion. The alternative Polθ-dependent TLS operates in an error-prone manner. (B) TLS pathways for replication through εdA. After nt insertion by Polι, Polζ extends synthesis. Polλ’s scaffolding role is required for Polζ function in TLS. This pathway operates in an error-free manner. Polθ-dependent TLS provides the other major TLS pathway and TLS requiring Rev1 polymerase function contributes to a relatively minor pathway. Polθ and Rev1 polymerase–dependent TLS operate in an error-prone manner. The thickness of the arrows depicts the relative contribution of TLS Pols to lesion bypass.