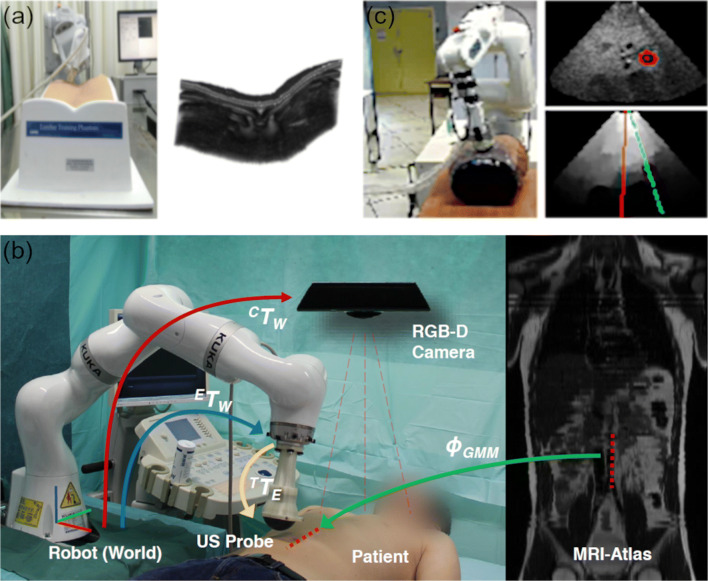
Fig. 3.
Overview of different robotic ultrasound systems for autonomous image acquisition. a A robotic ultrasound system autonomously scanning along a lumbar phantom (left) and the reconstructed ultrasound volume from 2D images (right) (copyright © [2019] IEEE. Reprinted with permission from [42]). b System setup including transformations (arrows) between robot, camera, ultrasound probe, and patient (left). MRI atlas displaying the generic trajectory (dotted red line) to image the aorta (right) (copyright © [2016] IEEE. Reprinted with permission from [44•]). c Robotic ultrasound system and phantom (left) with the target (red) in the ultrasound image (top right). A confidence map is calculated, and the current and desired configuration (red and green line, respectively) are calculated (bottom right) (copyright © [2016] IEEE. Reprinted with permission from [49])