Fig. 1.
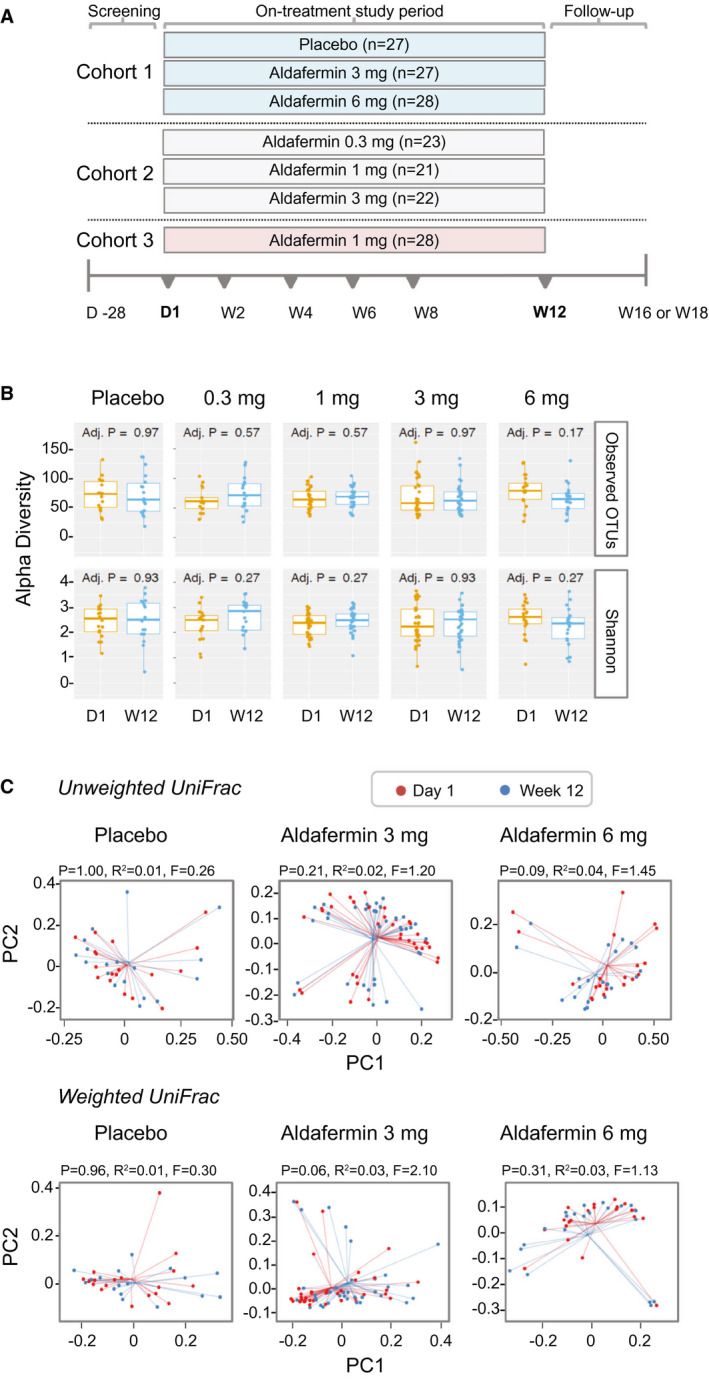
Stable gut microbiome with aldafermin therapy in patients with NASH. (A) Study design. Cohort 1 was a placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study comparing aldafermin 3 mg and 6 mg versus placebo for 12 weeks; cohort 2 was a dose‐expansion study evaluating aldafermin 0.3 mg, 1 mg, and 3 mg for 12 weeks; and cohort 3 further expanded the assessment of aldafermin 1 mg in additional patients for 12 weeks. Overall, a total of 176 patients with NASH received 0.3 mg (n = 23), 1 mg (n = 49), 3 mg (n = 49), or 6 mg (n = 28) aldafermin or placebo (n = 27) for 12 weeks in this phase 2 trial of aldafermin. The 16S rRNA sequencing of fecal samples collected at baseline (day 1) and week 12 (end of treatment) was performed. Patients had liver biopsy at baseline and underwent MRI and laboratory tests at baseline and week 12. (B) Gut microbial richness and evenness measured by alpha diversity (P values by Mann‐Whitney U test with FDR corrections using Benjamini‐Hochberg method). (C) Gut microbial beta biodiversity. Beta diversity was evaluated using UniFrac‐based analysis. In the principal coordinates analysis, no clustering was observed at the PC1 versus PC2 plot, indicating stable phylogenetic composition of the samples. All patients with paired stool samples at both day 1 and week 12 were included in the analysis: placebo (n = 18), aldafermin 0.3 mg (n = 17), 1 mg (n = 30), 3 mg (n = 36), and 6 mg (n = 21). Abbreviations: D1, day 1; W12, week 12.
