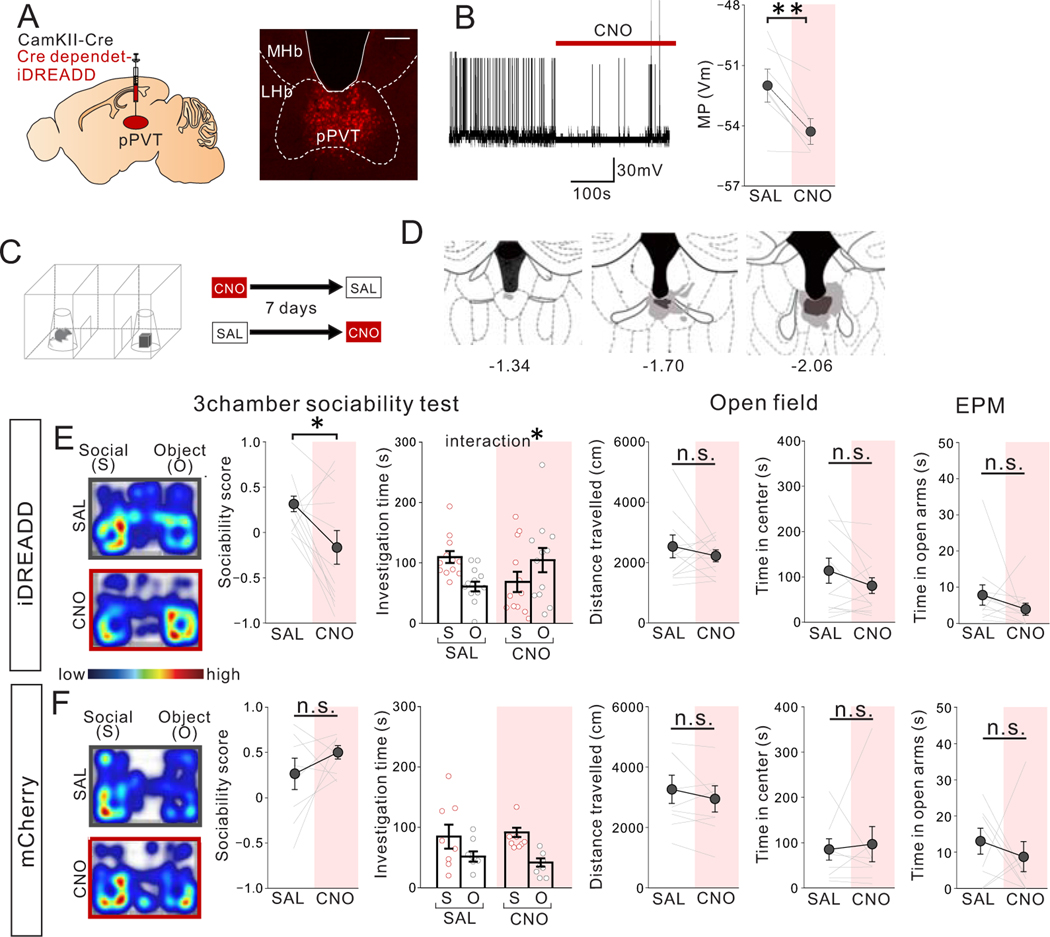
Extended Data Fig. 3. Chemogenetic suppression of pPVT neuron activity reduces sociability in adult group-housed mice.
(A) (left) AAV8-DIO-iDREADD (or mCherry) was injected together with AAV1-CaMKII-Cre in the pPVT. (right) A representative image shows selective transduction at injection areas of pPVT. Scale bar: 300um. Experimental images were obtained from 12 mice, three images per mouse, with similar results obtained. (B) Validation of iDREADD action in pPVT neurons by slice whole-cell patch clamp recording. (left) A representative trace shows that bath application of CNO significantly decreases membrane potential of pPVT neurons. Traces were recorded from 7 cells from 3 biologically independent mice, with similar results obtained. (Right) Quantification shows a reduction in membrane potential after CNO application (two tailed paired t-test, t6=4.177, **P=0.006, n=7cells from 3 biologically independent mice). (C) Mice were treated with saline (SAL) or CNO (10mg/kg) and then underwent the 3 chamber test of sociability. For CNO and SAL injections, order is counter-balanced. (D) Viral spread validation at injection areas of pPVT from post-behavioral testing mice. Gray areas represent the minimum (lighter colour) and the maximum (darker colour) spread of iDREADD into the pPVT. (E) (left) CNO-treated iDREADD+ mice showed reduced sociability, revealed by reduced sociability scores vs. SAL (two tailed paired t-test, t11=2.257, *P=0.045, n=12 biologically independent mice), and disrupted behavior in 3 chamber sociability task (two-way RM ANOVA, housing (GH/jSI) × stimulus (social/object) interaction F1,22 = 4.894, *P=0.038, effect of drug F1,22 = 0.032, P=0.859, effect of stimulus F1,22 = 0.109, P=0.745, n=12 biologically independent mice). (right) iDREADD+ mice showed no differences in motor activity or anxiety-related behaviors (Left; two tailed paired t-test, t11=0.688, P=0.506, n=12 biologically independent mice Middle; two tailed paired t-test, t11=1.604, P=0.137, n=12 biologically independent mice, Right; two tailed paired t-test, , t10=1.096, P=0.299, n=11 biologically independent mice) as a result of CNO vs. SAL treatment. (F) (left) Control mCherry+ mice showed no difference in sociability score (two tailed paired t-test, t7=1.459, P=0.188, n=8 biologically independent mice) or investigation time (two-way RM ANOVA, housing (GH/jSI) × stimulus (social/object) interaction F1,14 = 0.352, P=0.563, effect of drug F1,14 = 0.024, P=0.880, effect of stimulus F1,14 = 8.630, *P=0.011, n=8 biologically independent mice) as a result of CNO vs. SAL treatment. (right) Control mCherry+ mice showed no difference in motor activity or anxiety-related behaviors (Left; two tailed paired t-test, t7=0.981, P=0.359, n=8 biologically independent mice, Middle; two tailed paired t-test, t7=0.317, P=0.761, n=8 biologically independent mice Right: two tailed paired t-test, t7=0.662, P=0.529, n=8 biologically independent mice). Data in B, E, F are presented as mean +/− s.e.m.