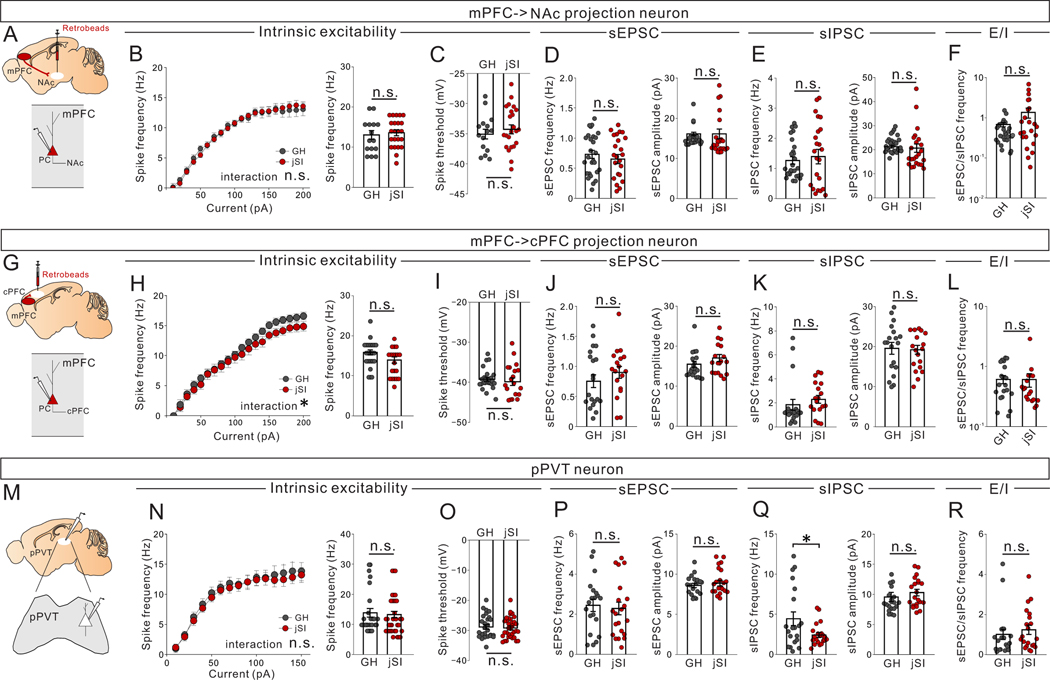
Extended Data Fig. 5. Juvenile social isolation does not change excitability, nor E/I input ratio of PFC->NAc neurons, mPFC->cPFC neurons, or pPVT neurons in adulthood.
(A-F) Whole-cell patch clamp recording from mPFC->NAc neurons in adult jSI or GH mice. (B, C) Assessment of intrinsic excitability of PFC->NAc neurons in the presence of DNQX, D-AP5, and picrotoxin. (B) (Left) Input-output curves showed no differences in spike frequency between jSI and GH mice (two-way RM ANOVA, housing (GH/jSI) x current step interaction F19,551 = 0.388, P=0.992, effect of housing F1,29 = 1.103, P=0.302, effect of current step F2.472, 71.70 = 161.200, P=0.001×10−12, n=15 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice). (right) No significant differences in spike frequency at 200pA between jSI and GH (two tailed t-test, t36=0.399, P=0.692, n=15 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice) (C) No significant differences in spike threshold between jSI and GH (two tailed t-test, t36=−0.708, P=0.484, n=15 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice). No significant differences in (D) sEPSC frequency (two tailed t-test, t48=0.308, P=0.760, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), sEPSC amplitude (two tailed t-test, t48=0.305, P=0.762, n=27 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), (E) sIPSC frequency (two tailed t-test, t48=0.879, P=0.384, n=27 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), sIPSC amplitude (two tailed t-test, t48=0.852, P=0.398, n=27 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells, from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), or (F) sEPSC/sIPSC frequency ratio (two tailed t-test, t48=1.767, P=0.084, n=27 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=23 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice) between jSI and GH. (G-L) Whole-cell patch clamp recording from mPFC->contralateral PFC projection neurons (cPFC) in adult jSI or GH mice. (H, I) Assessment of intrinsic excitability of PFC->cPFC neurons in the presence of DNQX, D-AP5, and picrotoxin. (H) (Left) Input-output curve showing no differences in spike frequency (two-way RM ANOVA, housing (GH/jSI) x current step interaction F19,798 = 1.861, *P=0.014, effect of housing F1,42 = 0.648, P=0.425, effect of current step F4.628, 194.4 = 395.9, P=0.001×10−12, n=26 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice). (right) No significant differences in spike frequency at 200pA between jSI and GH (two tailed t-test, t44=1.650, P=0.106, n=26 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice). (I) No significant differences in spike threshold (two tailed t-test, t44=0.635, P=0.529, n=26 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), (J) sEPSC frequency (two tailed t-test, t36=0.847, P=0.403, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=18 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), sEPSC amplitude (two tailed t-test, t36=1.370, P=0.179, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=18 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), (K) sIPSC frequency (two tailed t-test, t36=0.758, P=0.454, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=18 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice,), sIPSC amplitude (two tailed t-test, t36=0.493, P=0.625, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=18 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice), or (L) sEPSC/IPSC frequency (two tailed t-test, t36=0.147, P=0.884, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=18 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice) between jSI and GH. (M-R) Whole-cell patch clamp recording from pPVT neurons in adult jSI or GH mice. (N, O) Assessment of intrinsic excitability of pPVT neurons in the presence of DNQX (20μM), D-AP5 (50μM), and picrotoxin (30μM). (N) (Right) Input-output curve showing no differences in spike frequency (two-way RM ANOVA, housing (GH/jSI) x current step interaction F14,826 = 0.686, P=0.790, effect of housing F1,59 = 0.017, P=0.898, effect of current step F1.843, 108.7 = 93.580, P=0.001×10−12, n=26 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=35 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice). (left) No significant differences in spike frequency at 200pA (two tailed t-test, t59=0.434, P=0.666, n=26 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=35 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice), (O) spike threshold (two tailed t-test, t59=0.376, P=0.708, n=26 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=35 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice), (P) sEPSC frequency (two tailed t-test, t39=0.356, P=0.724, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=21 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice), or sEPSC amplitude (two tailed t-test, t39=0.636, P=0.529, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=21 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice) between jSI and GH. (Q) sIPSC frequency was significantly higher in jSI mice compared to GH mice (two tailed t-test, t39=2.316, *P=0.026, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=21 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice), but no differences in sIPSC amplitude (two tailed t-test, t39=1.804, P=0.079, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=21 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice) were observed. (R) No significant differences in sEPSC/IPSC frequency from pPVT neurons (two tailed t-test, t39=0.682, P=0.499, n=20 cells from 8 biologically independent GH mice, n=21 cells from 9 biologically independent jSI mice) between jSI and GH. Data in B-F, H-L, N-R are presented as mean +/− s.e.m.