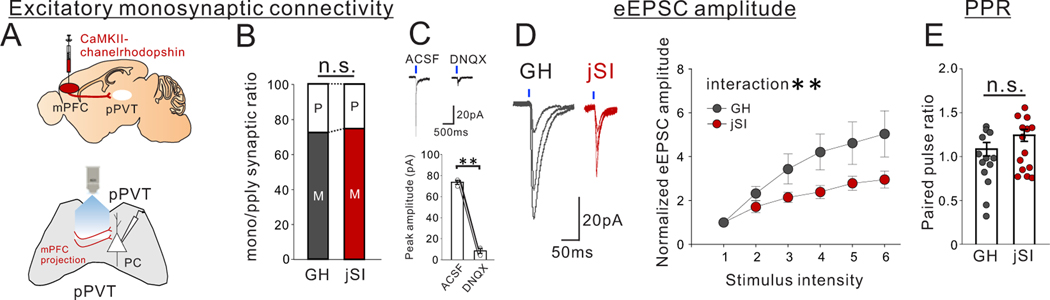
Extended Data Fig. 7. Optogenetic interrogation of mPFC->pPVT projection inputs onto pPVT neurons.
(A) ChR2-encoding AAV1 was injected into the mPFC to express ChR2 in mPFC neurons. Whole cell patch-clamp recordings were performed while optogenetically activating mPFC->pPVT projection terminals in pPVT slices. (B) Excitatory connectivity was assessed by normalized postsynaptic currents (PSCs) recorded at −70 mV from pPVT neurons before and after application of tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1 μM) with 4-aminopyridine (4-AP; 100 μM). A majority of pPVT neurons received a monosynaptic input from mPFC. There was no difference in mono/polysynaptic ratio (two tailed t-test, t13=0.349, P=0.733, n=8 cells from 5 biologically independent GH mice, n=7 cells from 5 biologically independent jSI mice). (C) (upper) Representative traces showing that optogenetic activation of mPFC->pPVT axons blocked by DNQX (20 μM). pPVT neurons were clamped at –70 mV while optogenetically stimulating mPFC-pPVT axons before and after bath application of DNQX. Traces are recorded from 3 cells from 2 biologically independent mice, with similar results obtained. (bottom) Averaged amplitude decreases after application of DNQX (two tailed t-test, t2=17.790, **P=0.003, n=3 cells from 2 biologically independent mice). (D) (left) Representative eEPSC of pPVT neurons upon optogenetic activation of mPFC->pPVT axons in GH and jSI mice through gradually changing the intensity. Traces were recorded from 17 cells from 7 biologically independent mice per group, with similar results obtained. (right) Intensity–amplitude curves showing the relationship between stimulus intensity and normalized eEPSC amplitude. Normalized eEPSC amplitude was lower in jSI mice than GH mice (two-way RM ANOVA, housing (GH/jSI) x current step interaction F5,185 = 3.740, **P=0.003, effect of housing F1,37 = 4.173, P=0.048, effect of current step F1.224, 45.29 =25.830, P=0.174×10−5, n=17 cells from 7 biologically independent GH mice, n=17 cells from 7 biologically independent jSI mice). (E) There were no significant differences in PPR at a 500-ms interval (two tailed t-test, t25=1.551, P=0.134, n=17 cells from 7 biologically independent GH mice, n=21 cells from 8 biologically independent jSI mice). Data in C, D, E are presented as mean +/− s.e.m.