FIGURE 5.
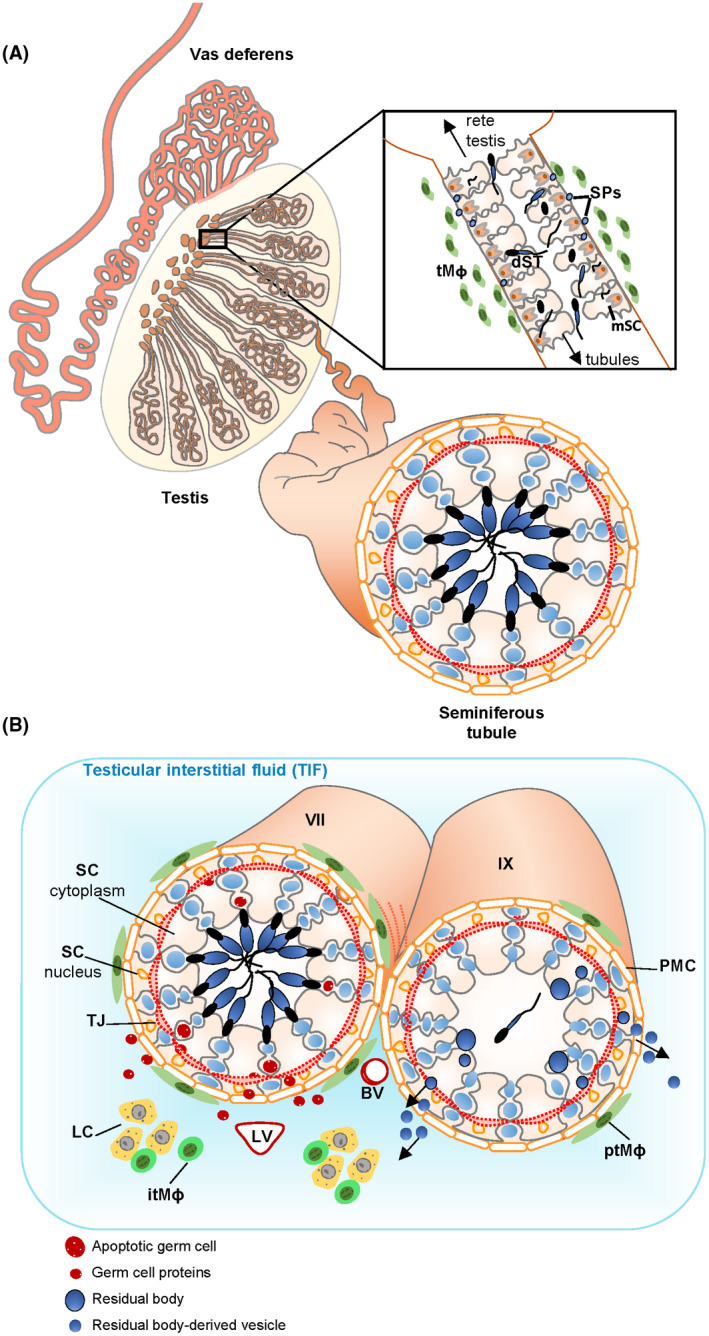
Model of sperm protein deposition into TIF. A, Diagram of the sperm‐producing seminiferous tubules that are coiled inside the testis, Inset: the tubuli recti are short segments of modified tubules at the end of the seminiferous tubules as they terminate at the rete testis. These tubules contain a narrow lumen and an epithelium of modified Sertoli cells (mSC). Fragments of degenerating sperm (dST) often appear in the epithelium and sperm proteins (SPs) are hypothesized to exit the tubules due to a weak epithelial barrier. 77 MHCII+ testicular macrophages (tMɸ) are concentrated around this site in the normal testis. B, The seminiferous tubules are surrounded by basement membrane and peritubular myoid cells (PMC); inside the tubules, the seminiferous epithelium is comprised of the somatic Sertoli cells (SC) and the male germ cells (shown in blue) at various stages of development. Tight junctions (TJ) between Sertoli cells prevent the free passage of molecules into and out of the tubules. Thus, the inner‐tubule milieu is strictly determined by the seminiferous epithelium; this site is known as the adluminal compartment of the tubules. The testicular interstitial fluid (TIF) surrounds the tubules; the interstitium contains the steroidogenic Leydig cells (LC), blood vessels (BV), lymphatic vessels (LV), and spherical, MHCII‐ interstitial testicular macrophages (itMɸ). Elongated MHCII+ peritubular macrophages (ptMɸ) surround the seminiferous tubules, with the number of macrophages varying according to the stages of germ cell development. 65 After mature sperm are released from the tubules, remnants of their cytoplasm known as residual bodies are phagocytosed and processed; some of the contents of these residual bodies are proposed to be released in residual body‐derived vesicles from stage IX tubules (IX) and to promote peripheral tolerance. 23 We hypothesize that germ‐cell proteins could also be released from stage VII tubules (VII) where there is continual apoptosis of a small percentage of spermatocytes and round spermatids. MHCII+ peritubular macrophage numbers are highest around this stage 65
