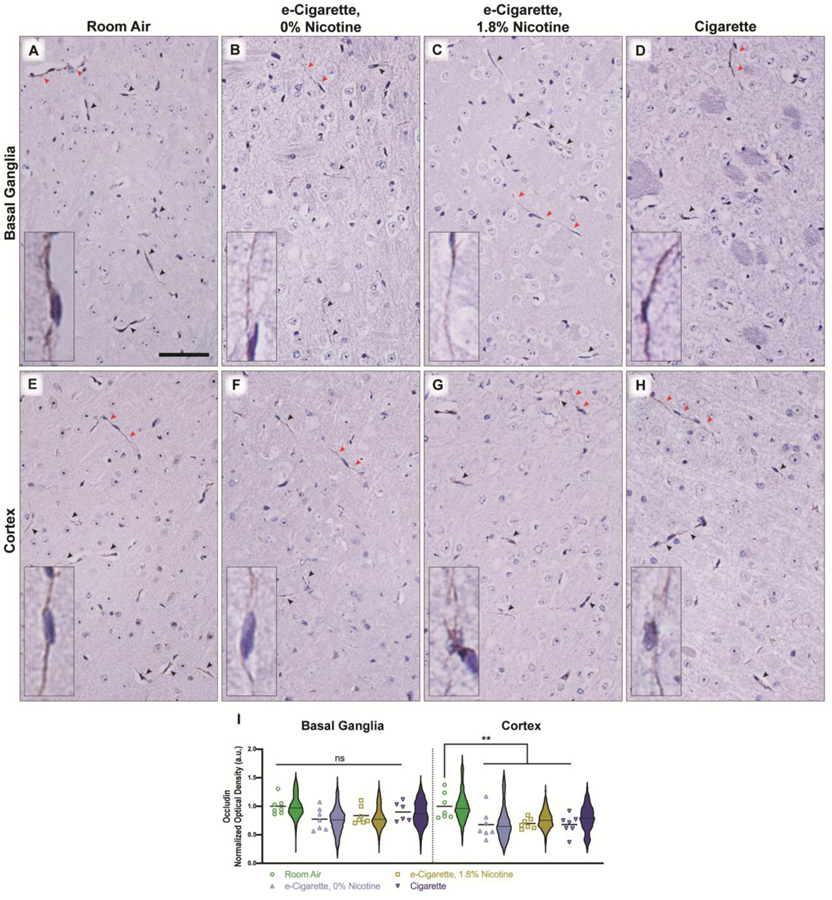
Figure 4.
Localization of Occludin is disrupted in vessel tight junctions of the cortex following exposure to e-cigarettes or cigarettes. Whole tissue scans were captured from rostral coronal sections, and separated by region for analysis. Representative images from basal ganglia (A-D) and cortex (E-H) are shown for each treatment group and Occludin-positive microvessels are indicated by arrowheads. Red arrowheads indicate vessels which are shown in the high-magnification inset. Occludin-positive areas were identified by thresholding of red-to-blue ratio value across each brain region of interest, and densitometry values of Occludin-positive area (I) were quantified and normalized to the whole region for basal ganglia and cortex. Mean densitometry of all vessels per animal is shown by individual points (n = 6–7 mice/group) with cross-bar indicating mean of all animals. Violin plots depict the distribution of densitometry for all detected vessels within a treatment group (n = 2465–4839 vessels/group). Statistics were carried out using only individual animal means. **, p < 0.01; ns, no significance versus room air. Two-way ANOVA was applied [exposure, F(3,47)=6.310, p=0.0011; region, F(1,47)=0.0249, p=0.0249); interaction, F(3,47)=0.8543, p=0.4714]. Scale bar, 25 μm.